Developer Guide
By: CS2113T-M16-2 Since: 2020


- Developer Guide
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Setting up
- 3. Design
- 4. Implementation
- Appendices
- Appendix A: Product Scope
- Appendix B: User Stories
- Appendix C: Value proposition - Use cases
- Appendix D: Non-Functional Requirements
- Appendix E: Glossary
- Appendix F: Instructions for Manual Testing
- F.1. Launch and Shutdown
- F.2. Add an ingredient
- F.3. List ingredient
- F.4. Delete an ingredient
- F.5. Search for ingredient
- F.6. Add a recipe
- F.7. List recipe
- F.8. Cook a recipe
- F.9. Delete a recipe
- F.10. Search for recipe
- F.11. Add a chore
- F.12. List chore
- F.13. Delete a chore
- F.14. Search for chore
- F.15. Mark a chore as done
- F.16. Saving data
- F.17. Display expenditure
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Kitchen Helper, born from the need to keep track of kitchen inventory, is an application that is designed to manage kitchen inventory and chores. Users will be able to reduce food wastage and save money through the convenience of viewing the contents of the inventory.
1.2. Purpose
The document contains the specified architecture and software design specifications for the application, Kitchen Helper.
1.3. Scope
This describes the software architecture and software design requirements for Kitchen Helper. This guide is mainly for developers, designers and software engineers that are or going to work on Kitchen Helper.
2. Setting up
2.1. Prerequisites
- JDK
11. - IntelliJ IDE.
2.2. Setting up the project in your computer
- Fork this repository, and clone the fork repository to your computer.
- Open Intellij (if you are not in the welcome screen, click
File>Close Projectto close the existing project dialog first). - Set up the correct JDK version for Gradle
- Click
Configure>Structure for New Projectsand thenProject Settings>Project>Project SDK. - If
JDK 11is listed in the drop down, select it. Otherwise, clickNew…and select the directory where you installedJDK 11. - Click
OK.
- Click
- Click
Import Project. - Locate the
build.gradlefile and select it. ClickOK. - Click
Open as Project. - Click
OKto accept the default settings if prompted.
3. Design
This section provides a high level overview of our application, Kitchen Helper.
3.1. Architecture
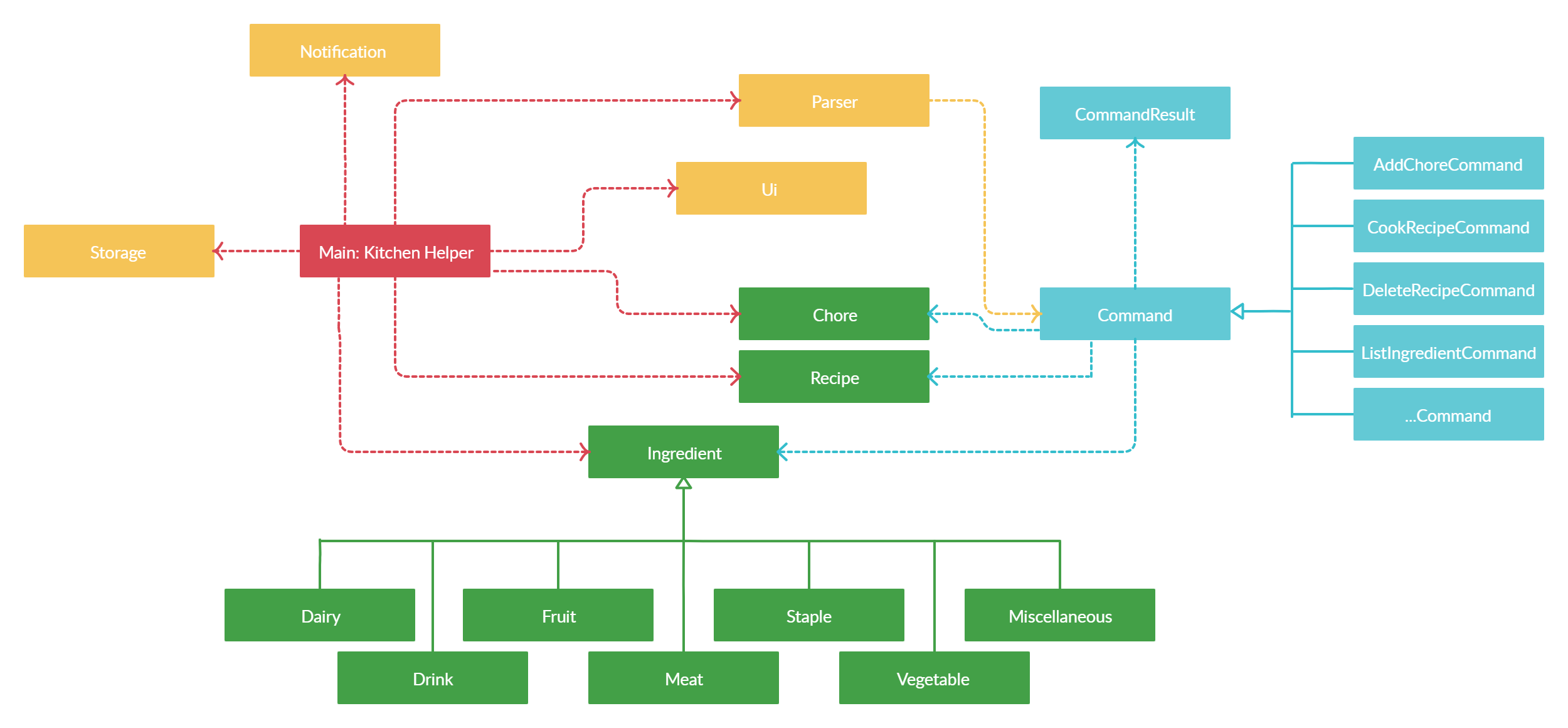 The image above explains the design of the application, Kitchen Helper.
The image above explains the design of the application, Kitchen Helper.
The main driver of the application is Main: Kitchen Helper. It is responsible for mainly two phases:
- At application launch
- This class will initialise the components in the correct sequence and is in charge of connecting them with each other.
- At shut down
- This class will invoke cleanup method for the components when necessary.
In addition to that, the architecture of Kitchen Helper is broken down into seven classes, mainly the following:
Ui: This class mainly handles the UI of the application.Parser: This class mainly handles the parsing and handling of user commands.Command: This class handles the type of command.Ingredient: This class manages the data of data type ingredient in memory.Chore: This class manages the data of data type chore in memory.Recipe: This class manages the data of data type recipe in memory.Storage: This class reads data from and writes data back into a text file for future uses.
3.2. Ui Component
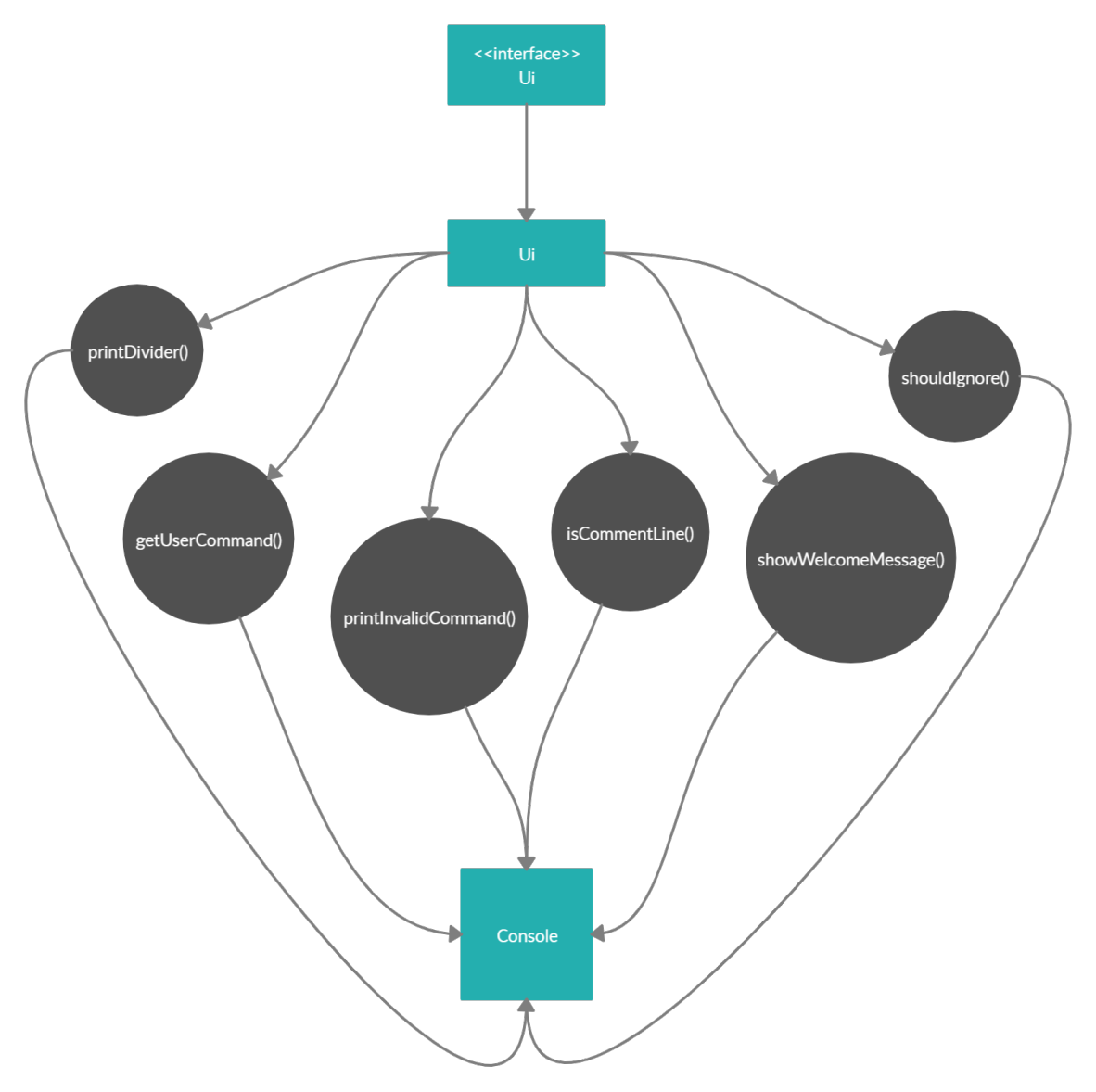
API: Ui.java
The Ui component is a singleton class where all interaction will be made through this component
The Ui component,
- Executes user commands using the command component
- Listens for changes and outputs messages from the Command component
3.3. Logic Component
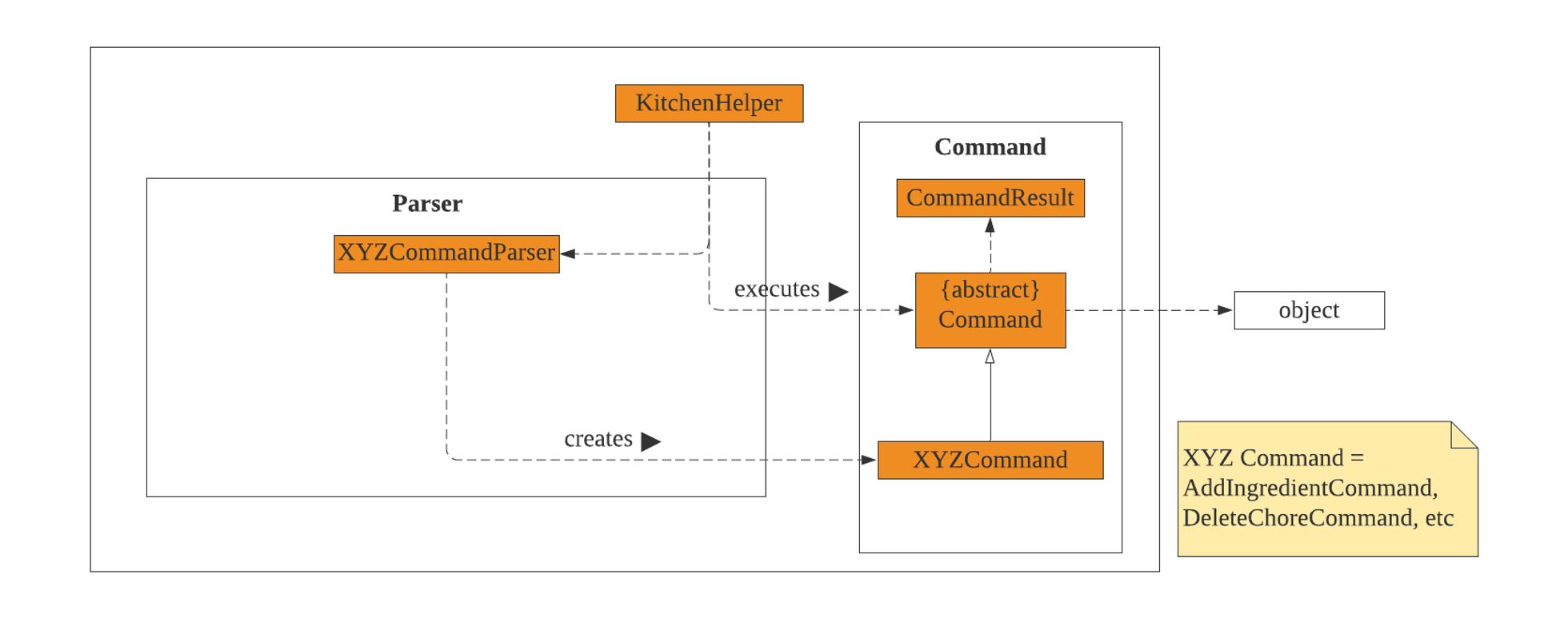
Kitchen HelperusesParserclass to parse the user command.- This results in a command object return back which is executed by
Kitchen Helper. - The command execution can affect the object (e.g. adding an ingredient).
- The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is passed back toUito display the message.
3.4. Model Component
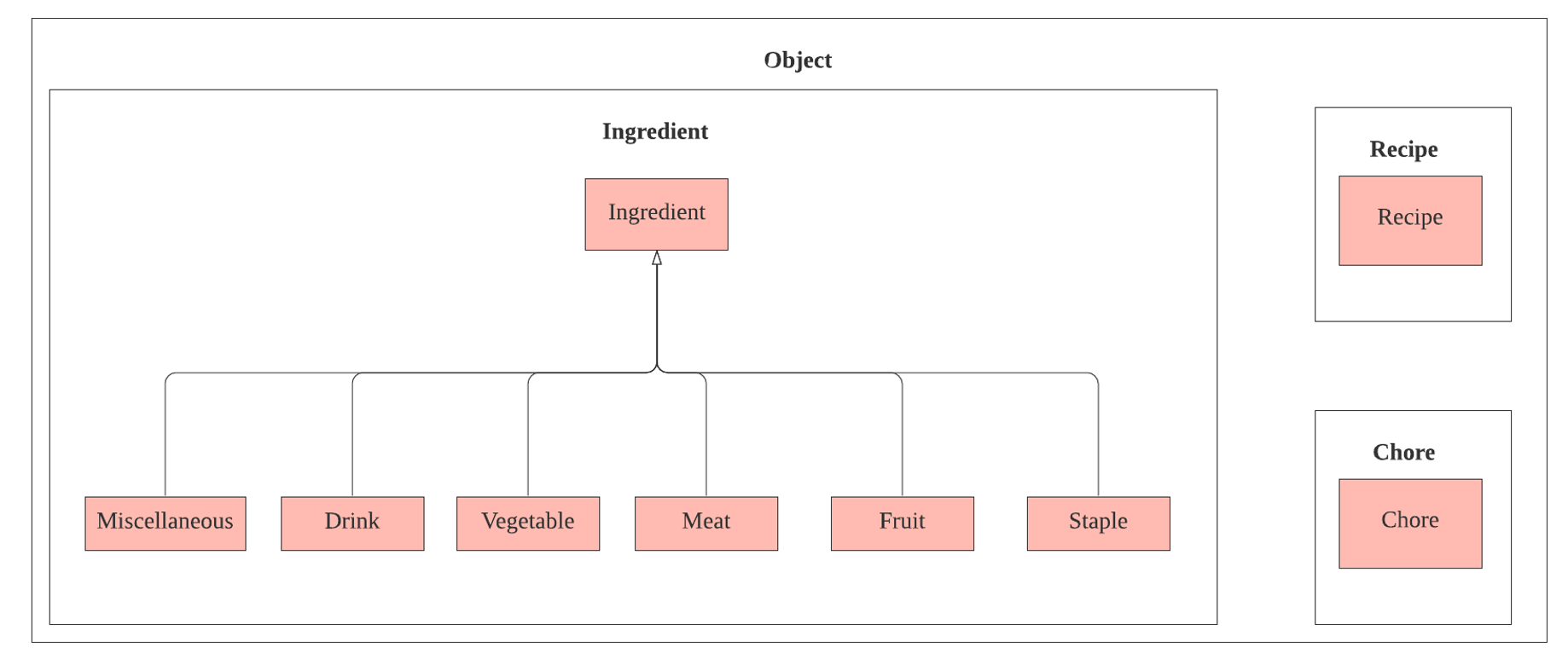
The Model component contains Ingredient, Recipe and Chore classes, which store the user’s input in Kitchen Helper.
- Ingredient: Stores the ingredient data.
- Recipe: Stores the recipe data.
- Chore: Stores the chore data.
3.5. Storage Component
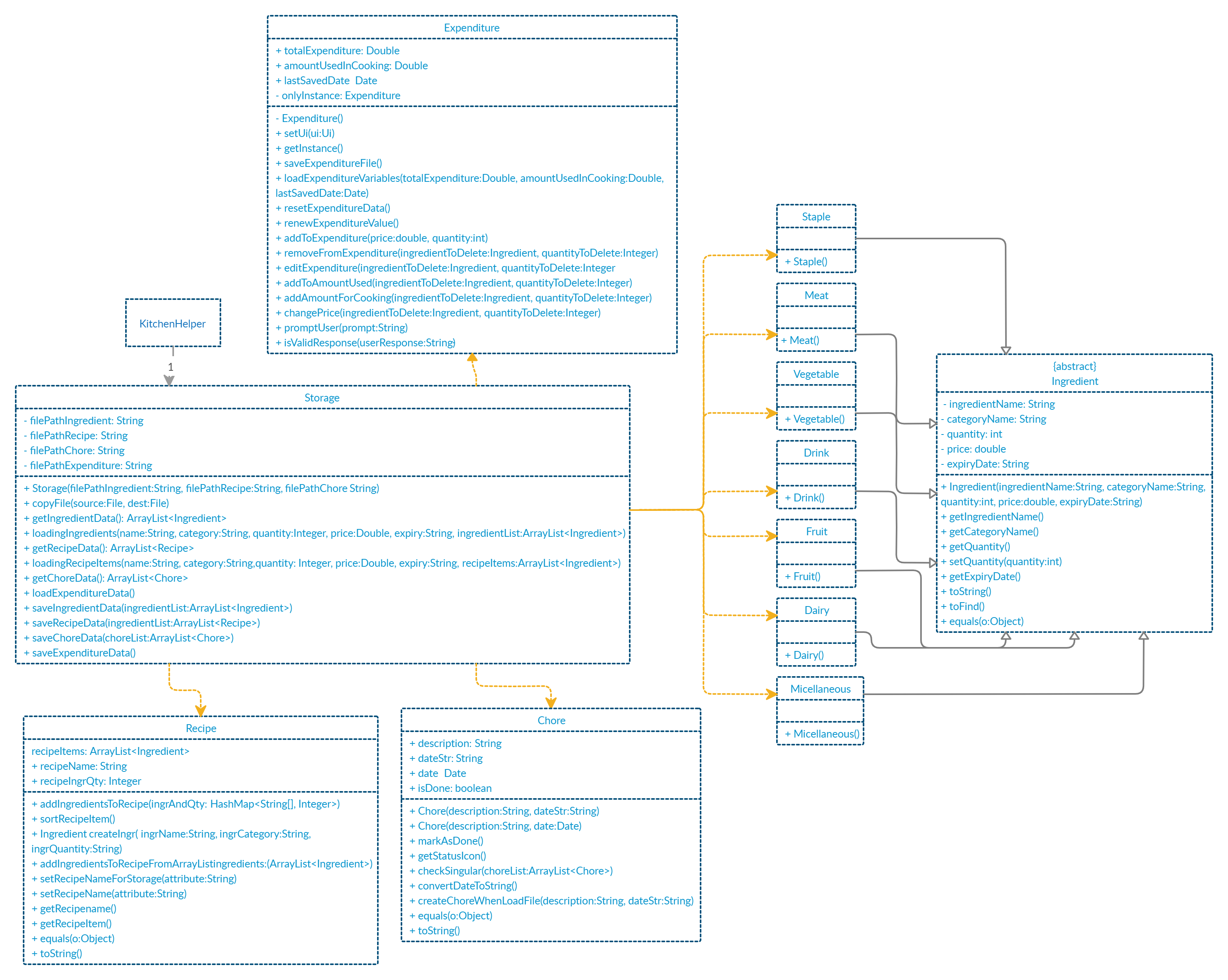
A Storage object is created by the KitchenHelper class to handle the loading and saving of ingredients, recipes, chores and expenditure data.
The Storage() method acts as a constructor with filepaths to local save files for ingredients, recipes, chores and expenditure data.
The getIngredientData(), getRecipeData(), getChoreData() and loadExpenditureData() methods are used to read saved data from local files into the current session of KitchenHelper. loadingIngredients() and loadingRecipeItems() methods are called in getIngredientData() and getRecipeData() respectively to sort out which Ingredient object class each object belongs to.
The saveIngredientData(), saveRecipeData(), saveChoreData() and saveExpenditureData() methods write the current state of KitchenHelper into the local save files by calling them in various command classes such as AddChoreCommand and DeleteIngredientCommand.
3.6. Common Classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.kitchenhelper.object package.
4. Implementation
This section describes some details on how the features are being implemented. All recipe/ ingredient/ chore-related features can be broken down into 4 distinct functionality, addition, listing, deletion and searching.
4.1.Ingredient-related Features
4.1.1. Addition of ingredient
The addition of the ingredient feature allows the user to keep track of the ingredients in the ingredient’s list.
For example, addingredient /n beef /c meat /q 2 /p 20 /e 18/02/2020 will add the ingredient beef
which have the following attributes: category meat, quantity 2, price $20 and expiry 18/02/2020
Implementation
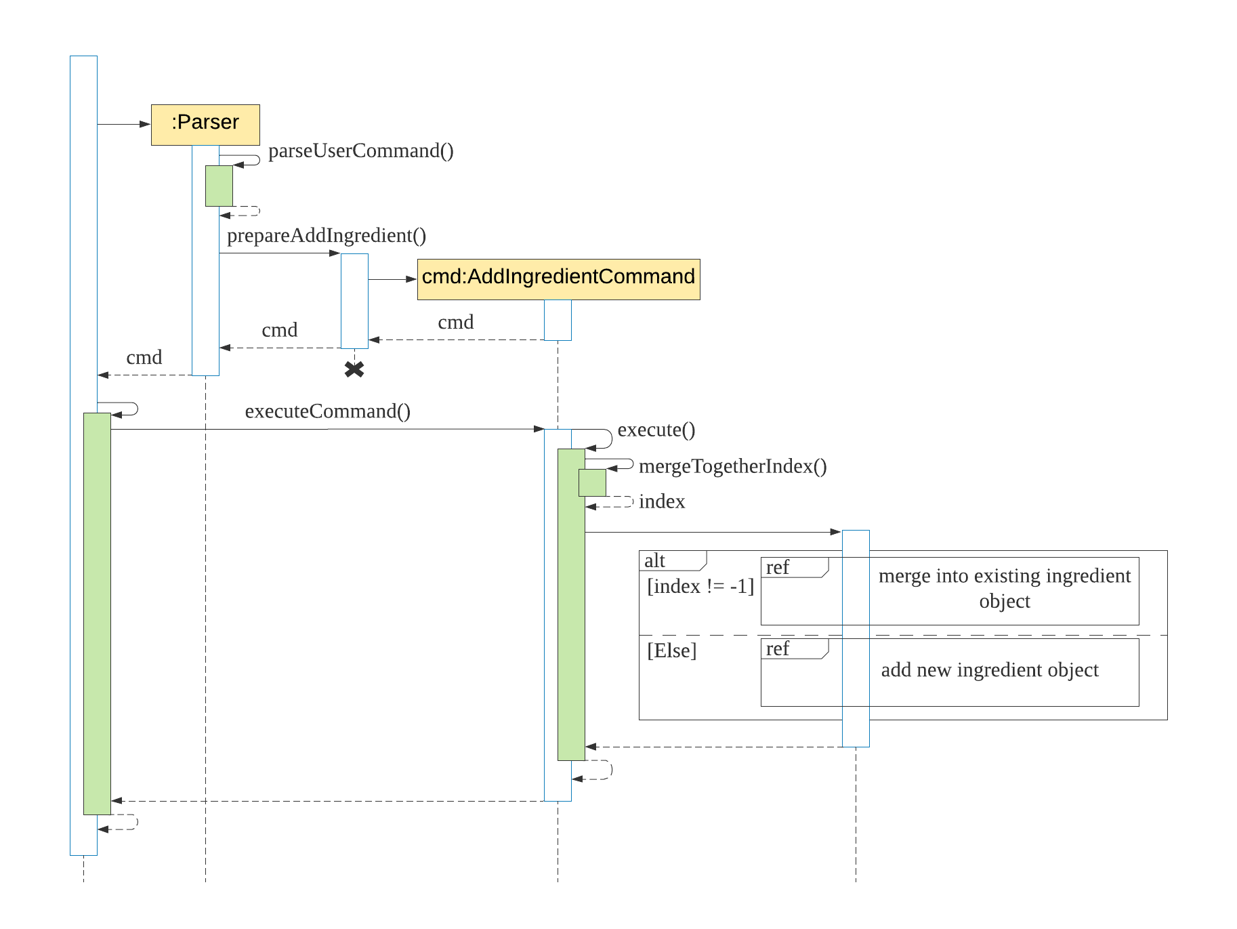
The following steps explained “Sequence diagram for an example addingredient command”:
- The user enters
addingredient /n beef /c meat /q 2 /p 20 /e 18/02/2020. KitchenHelpercallsParser#parseUserCommand().Parser#parseUserCommand()will call its own methodParser#prepareAddIngredient().Parser#prepareAddIngredient()will first validate the attributes and create an objectAddIngredientCommandwith the attributes if successful.KitchenHelpercalls it own methodexecuteCommand()to execute the method inAddIngredientCommand#execute().- On
AddIngredientCommand#execute(), ingredient is added and return of the message.
4.1.2. List all/ specific ingredient(s)
The list feature allows showing details of Ingredients added by the user. All ingredients added will be shown in a sorted order, by expiry, and shown by categories. The function will require a valid string , which belongs to all/dairy/drink/fruit/meat/miscellaneous/staple/vegetable,
to be added as a parameter. Failure to do so will trigger an exception where the user will be notified of an invalid command and the syntax of the listing of the ingredients will be displayed.
Implementation
When the user attempts to list the details of a particular category of ingredients, the listIngredientCommand, ‘Parser’ and Ingredient class will be accessed and the following sequence of actions are called to list details of a particular category Ingredient list:
The following image below shows the sequence of steps for step 1 and 2:
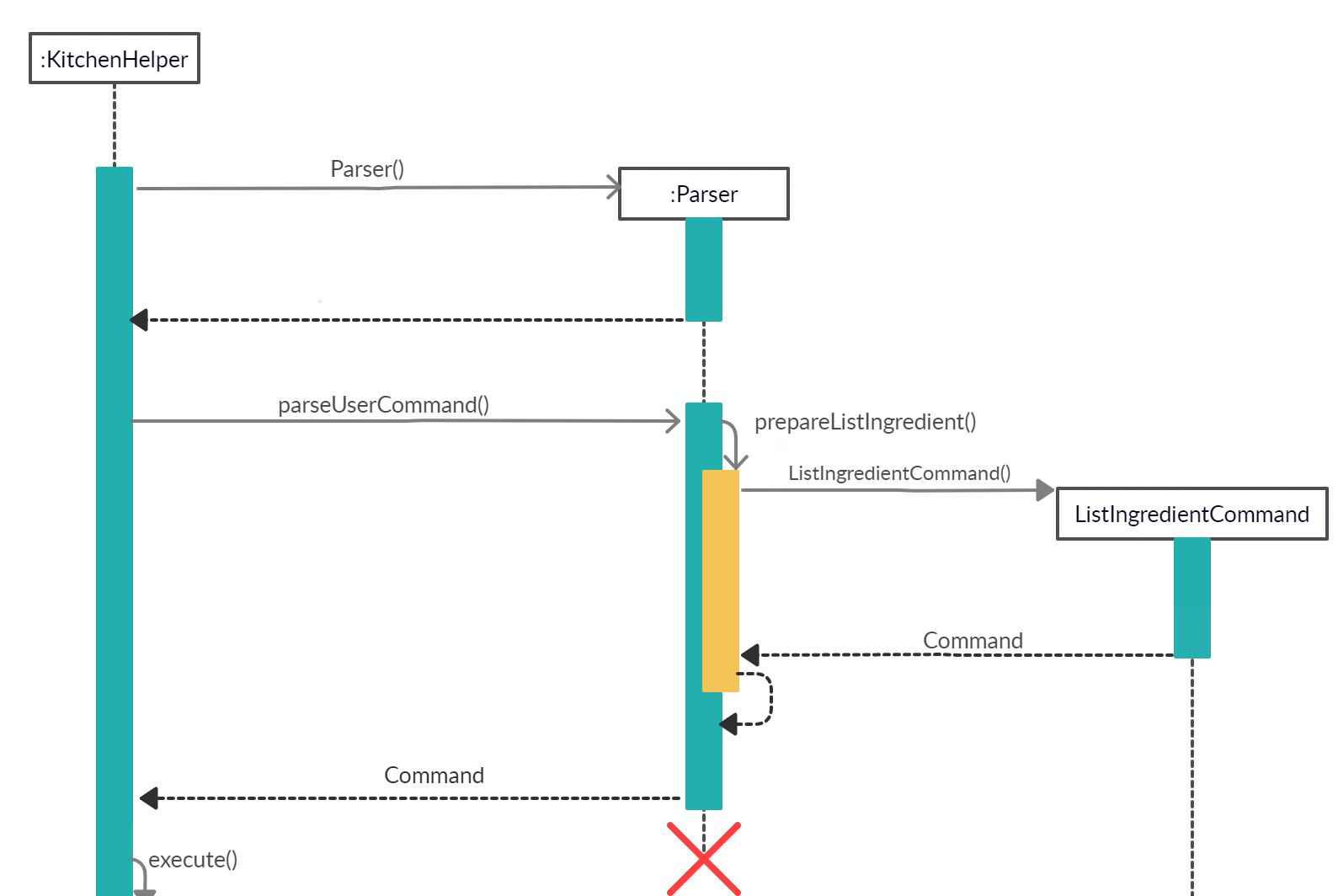
- User executes
listingredient all- A
Uiobject will be created and callsUi#getUserCommand() - Input will be parsed in
Command#parseUserCommand()and identified with the keywordlistingredient.
- A
- Parsing of user input and creation of command object
2.This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string into a suitable format for the listing of a particular category of
ingredientobject inCommand#prepareListIngredient().- A
ListIngredientCommandobject will be created.
- A
-
Executing Command The following image below shows the sequence for the next steps:
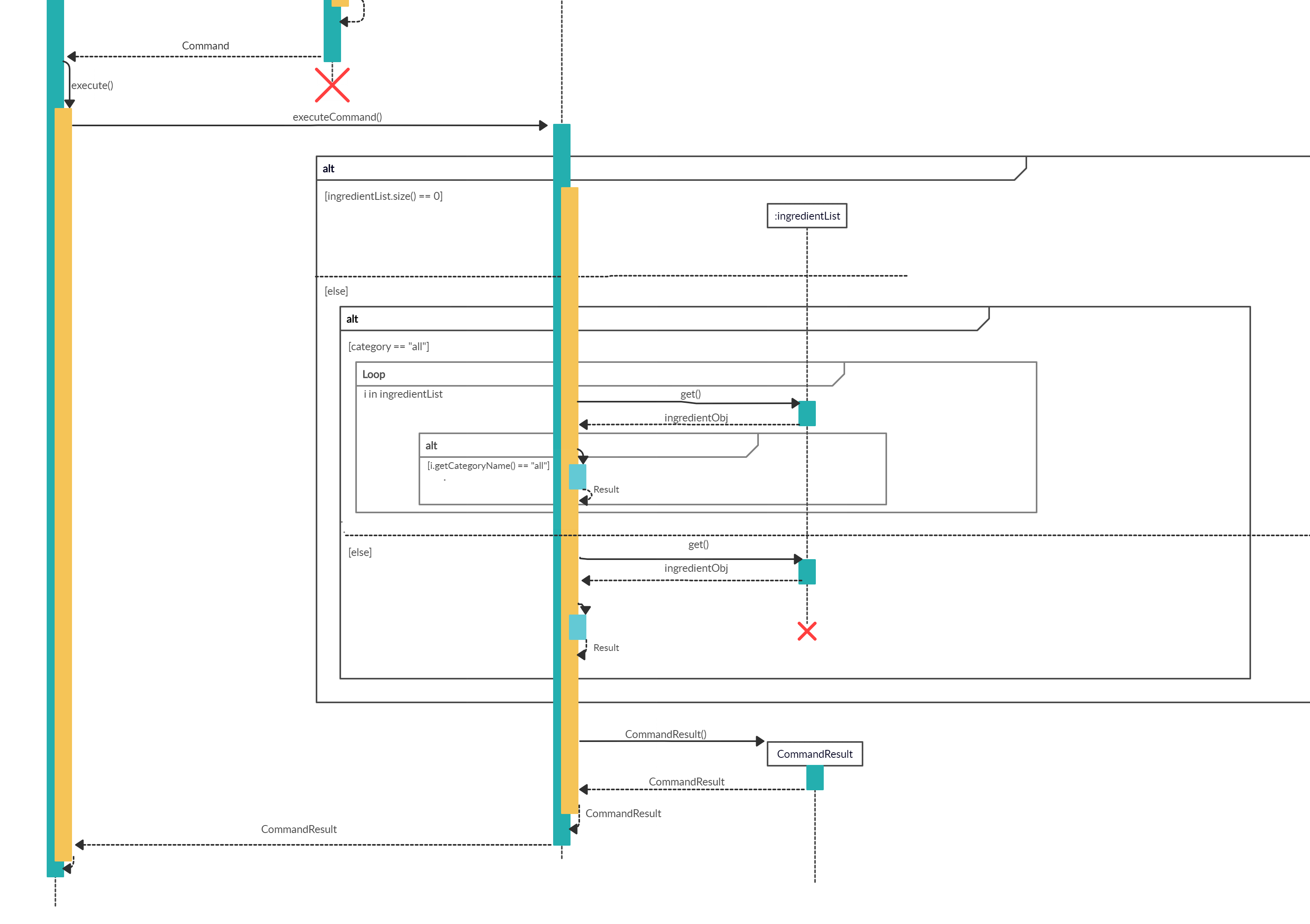
- The newly created object will call
#ListIngredientCommand#executewhich starts the process of listing a particular category’s ingredient details, thus callingListIngredientCommand#listIngredients(). - The existing ingredientList arraylist and the category of the chosen ingredient category will be passed through to the
ListIngredientCommand#listIngredients(). - The function will find if the category name is valid, thus, creates
CommandResultresult storing the details of the ingredient belonging to the particular category.
- The newly created object will call
- The details will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
The following shows the full sequence diagram for this command:
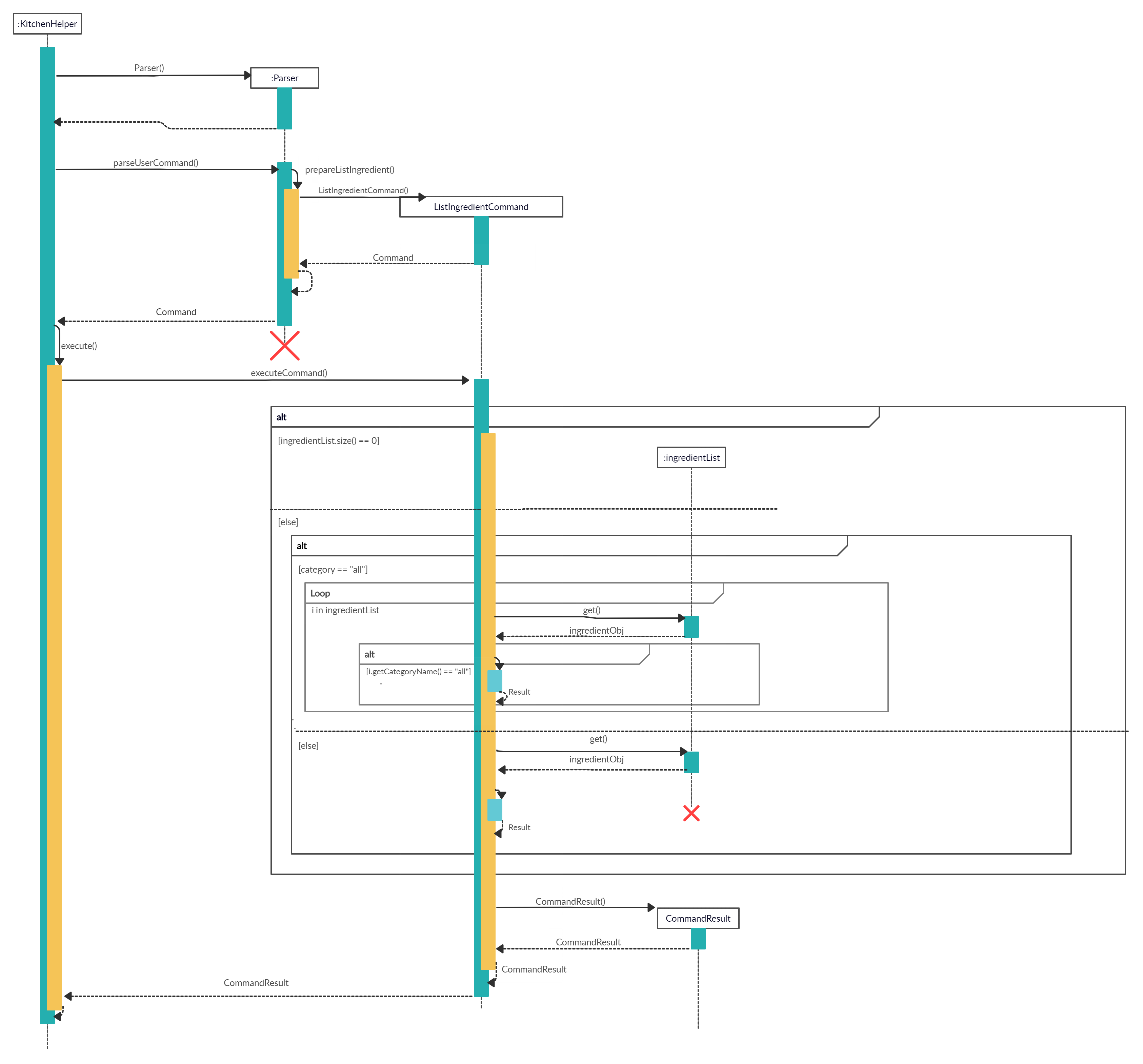
Design Considerations
Aspect: Finding the category name and print out ingredient belonging to the category
Alternative 1: Looping through the whole ingredientList arraylist to find out all possible category name, then, do sorting and return result
| Pros | The program will be able to detect all category name inside the ingredientList arraylist. |
| Cons | This method will be slow when facing a huge amount of data in the arraylist as the program may have to go through every single item in the arraylist. |
Alternative 2 (current choice): Creating a fixed array which includes the order and all possible category names.
| Pros | Users would be able to get the details of the particular recipe accurately and fast. |
| Cons | Program will not be able to handle any ingredient which isn’t belonging to the category names in the fixed array. |
4.1.3. Delete specific ingredients(s)
The deletion feature for ingredients allows the user to delete ingredients either by the name or index of the ingredients. In addition to that, it allows users to reduce the quantity of a specific ingredient.
Implementation
When the user attempts to reduce the quantity of ingredient at index 1 of the ingredients inventory by 4, the Kitchen Helper, Parser and DeleteIngredientCommand class will be called upon. The following sequence of steps will then occur:
The following image below shows the sequence of steps for step 1 and 2:
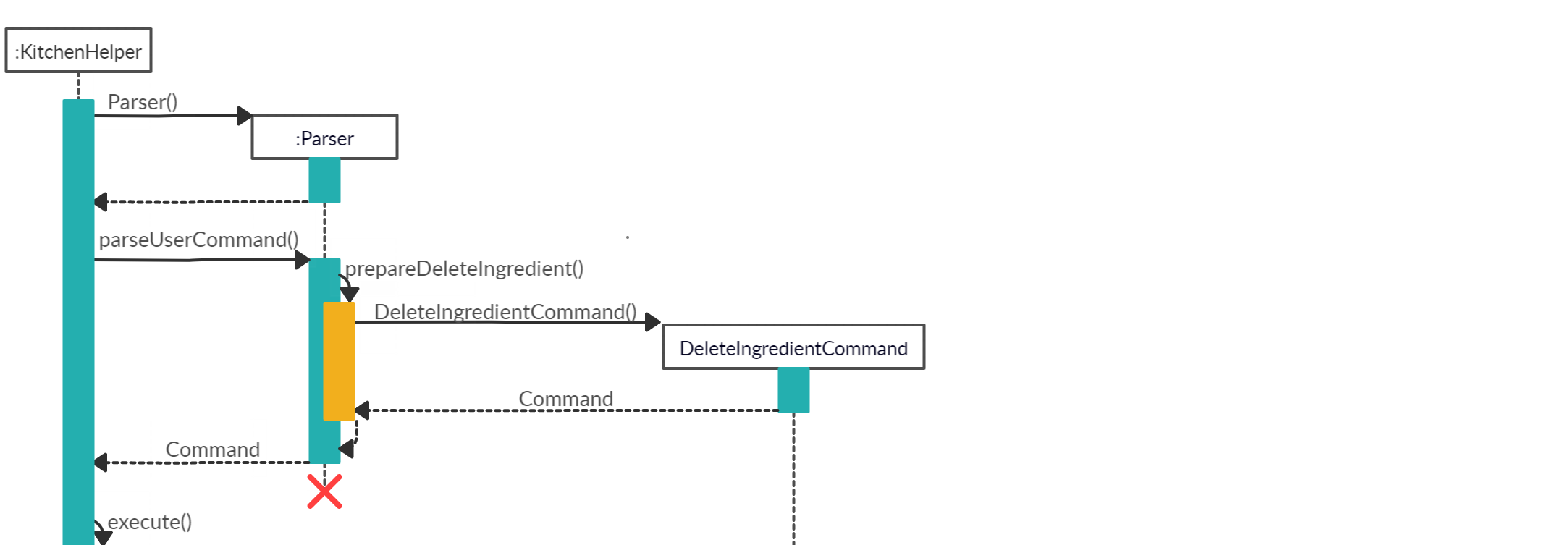
-
The user keyed in
deleteingredient /i 1 /q 4.- A
UIobject will be created and it will callUI#getUserCommand()method to take in the input that the user has keyed in. - A
Stringobject will be returned and saved into theuserCommandInputvariable inKitchen Helper. - The variable
userCommandInputis being parsed into theParserclass as an argument for this methodParser#parseUserCommand.

- A
-
The command inserted by the user is being parsed into the
Parserand a newCommandobject is being created.- The variable
userCommandInputwill be identified asdeleteingredientin theParser#parseUserCommand().TheParser#prepareDeleteIngredient()is being called to prepare theuserCommandInputstring to create aDeleteIngredientCommandobject. - The
DeleteIngredientCommandobject is created with the ingredientIndex and quantity set to 4.
- The variable
-
After creating
DeleteIngredientCommandobject, this Command will now be executed.The following image below shows the sequence for the next steps:
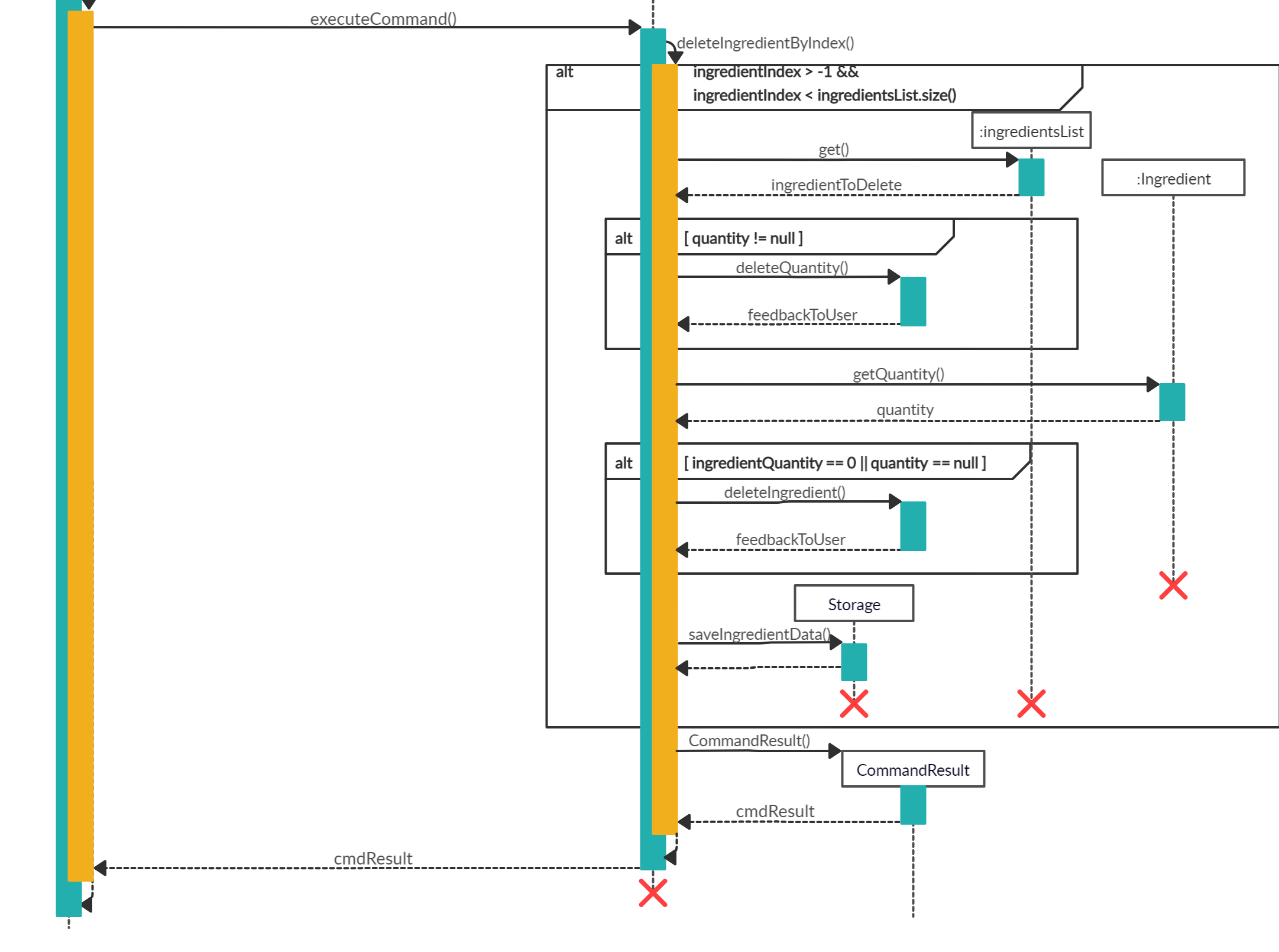
- The
DeleteIngredientCommand#execute()will be called which in turned calledDeleteIngredientCommand#deleteIngredientByIndex(). - Since the
quantityof this ingredient is not null, theDeleteIngredientCommand#deleteQuantity()will be called to reduce the quantity of this ingredient. - When
DeleteIngredientCommand#deleteQuantity()has returned, the program will get the quantity of the current ingredient after deduction. If the quantity is zero or null, theDeleteIngredientCommand#deleteIngredient()will be called to removeingredientfrom theingredientsListwhich contains all the ingredients. - Then,
Storage#saveIngredientData()will be called to save the currentingredientsListinto an output file. - Lastly, a String called
feedbackToUserwill be returned to the user to inform the user of the outcome of the command.
The following image shows the state diagram for the command execution:
- The
-
The details will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
The following shows the full sequence diagram for this command:
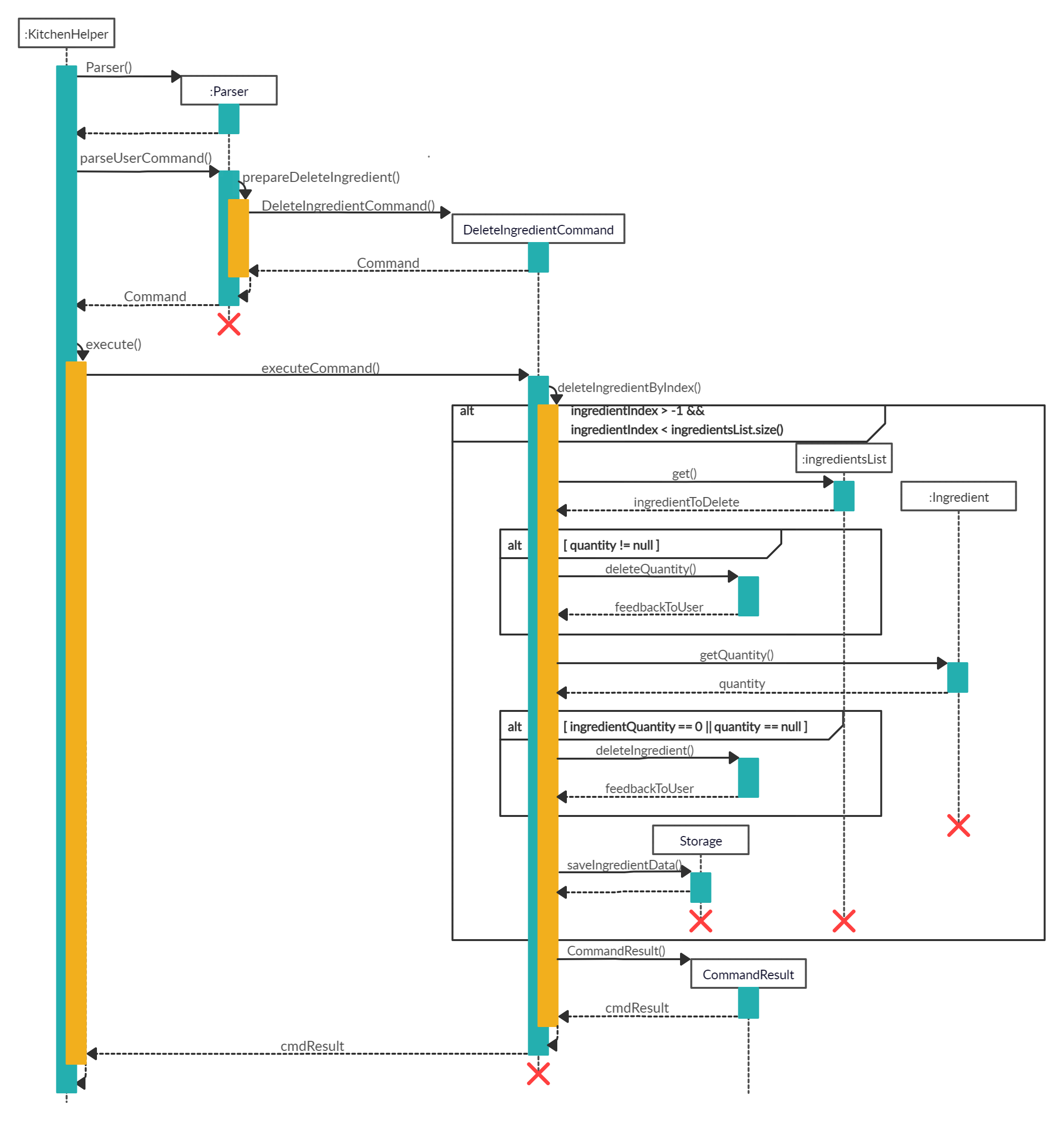
Other than deleting or reducing the quantity of an ingredient, DeleteIngredientCommand has an additional feature that is linked to Display Expenditure which will increase the cooking expenditure if the ingredients are used for cooking.
Design Considerations
- Aspect 1: How to differentiate
deleteingredientByQuantityanddeleteIngredient
-
Alternative 1 (Current Choice): The
quantityof ingredient inDeleteIngredientCommandconstructor is set to thequantitythat was inputted by the user. In the case where the user would like to delete an ingredient, thequantityvariable will be set tonull.Pros Only a quantityvariable needs to be set. This increases more convenience and no overload of constructors.Cons It is dependent on the variable to check if the ingredient is to be deleted. -
Alternative 2: Create 1 more constructor just for deduction of quantity for ingredients.
Pros This gives us more flexibility on what object can be created with different variables. Cons There may be an overload of constructors.
In the end, for
aspect 1. we have chosenalternative 1because there will not be an overload of constructors. -
- Aspect 2: Calling of function for deletion of
ingredientwheningredienthas the quantity of zero.-
Alternative 1 (Current Choice) : Two non-nested
if-elseblocks to cater fordeleteQuantityanddeleteIngredient.Pros SLAP is not violated. Cons Longer lengths of codes. -
Alternative 2: One nested
if-elseblock to cater fordeleteQuantityanddeleteIngredientPros Concise block of if-else.Cons The if-elseblock will be nested with anotherif-elseblock. This will violate the SLAP in code quality and the program will have to check for multiple conditions instead of one.
In the end, for
aspect 2, we have chosenalternative 1because there will be more concise blocks ofif-elsewhich helps to contribute to the non-violation of SLAP for the method. -
- Aspect 3: Deletion by index instead of name for ingredients
-
Alternative 1 (Current Choice): Deletion by index only
Pros Only a very specific ingredient can be deleted. Only need to get the ingredient from the list of ingredients by index. It is a more specific way to get the ingredient to delete. Cons Users will not be able to delete the ingredient by name. -
Alternative 2: Deletion by both index and name
Pros Users will be able to delete by ingredients’ name and index. Cons There may be confusion when it comes to the deletion by name for the users as the algorithm that was supposed to be implemented for deletion by name will delete the first instance of ingredient that is found. In the case, whereby the list of ingredients have two applesbut different expiry date and the user just want to delete the secondapplethat has a later expiry date. It will not be able to do so through deletion of name as the first instance ofappleis the one that has an earlier expiry date.
In the end, for
aspect 3, we have chosenalternative 1which is to delete by index for ingredients only so that the users can have a more convenient time in deleting the specific ingredient that they want to delete. However, deletion by name for ingredients may be implemented and enhanced in the future implementations once we have finalised our idea for its implementation. -
4.1.4. Search for ingredients based on keyword(s)
The search for ingredients feature allows the user to find ingredients using a keyword in the ingredient’s list.
For example, searchingredient beef will find all the ingredients that contain beef.
Implementation
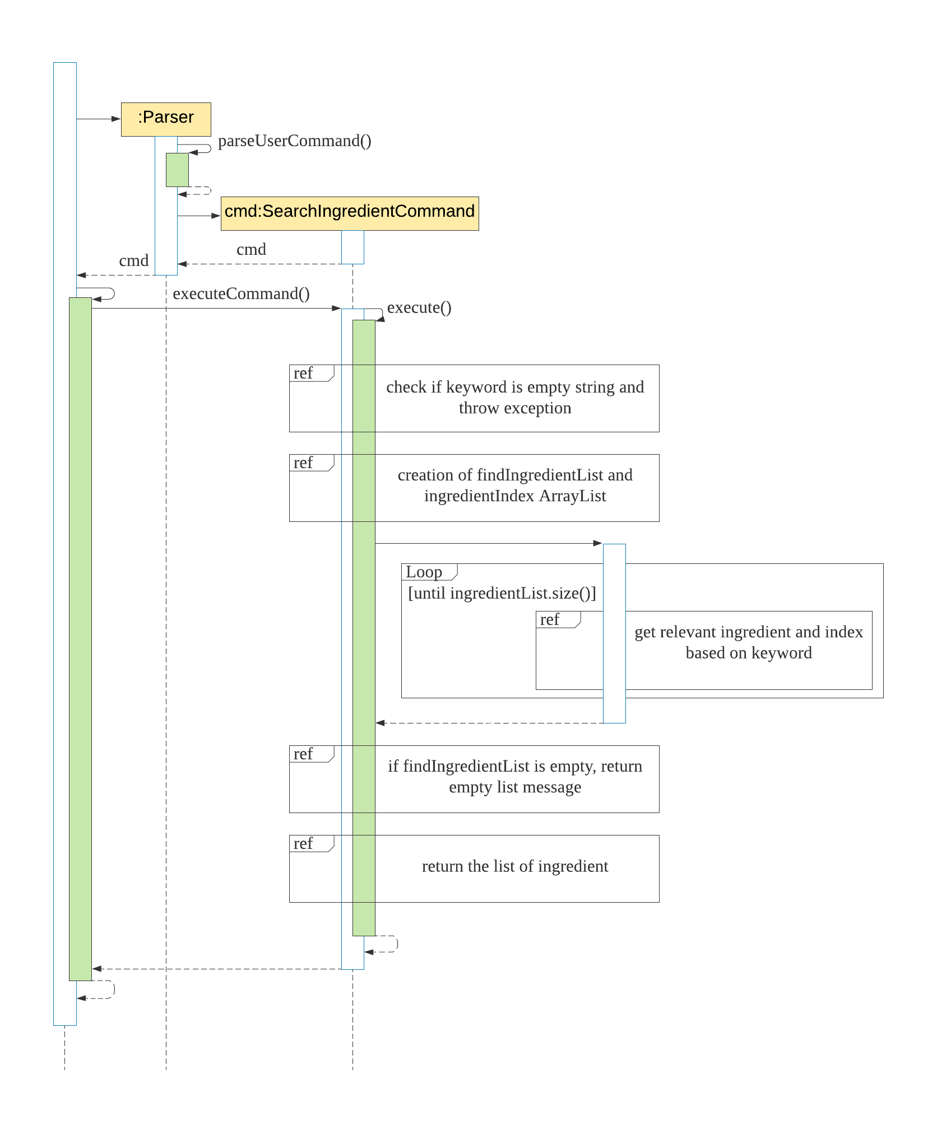
The following steps explained sequence diagram for searchingredient command:
- The user enters
searchingredient beef. KitchenHelpercallsParser#parseUserCommand().SearchIngredientCommandobject is created with the keyword passed in.KitchenHelpercalls it own methodexecuteCommand()to execute the method inSearchIngredientCommand#execute().- On
SearchIngredientCommand#execute(), display the list of ingredients that matches the keyword.
Design considerations:
Aspects: How searchingredient executes:
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Find if the keyword is part of the substring of the ingredient,
[Meat] Beef Qty:3 $20.00 Exp:18/03/2020.
| Pros | 1. Easily to find by any attributes such as category, ingredient’s name, quantity, price and expiry date. |
| Cons | 1. Searching beef [meat] will fail to show any matching result. |
- Alternative 2: Take in all the predicates given by the user and find using the predicates as a keyword
| Pros | 1. More accurate searching of the ingredient is available for the user. |
| Cons | 1. Requires users to enter more precise predicate keywords which could be more inconvenient. |
4.1.5. Notification for ingredients warning
The notification for ingredients warning runs everytime the program starts. Checks the ingredient list for ingredient that is expiring in 3 days, expired or low quantity (< 5).
For example, beef ingredient’s expired date is 02/02/2020 and have quantity of 3. The program will list down the ingredient in the categories when the application start.
Implementation
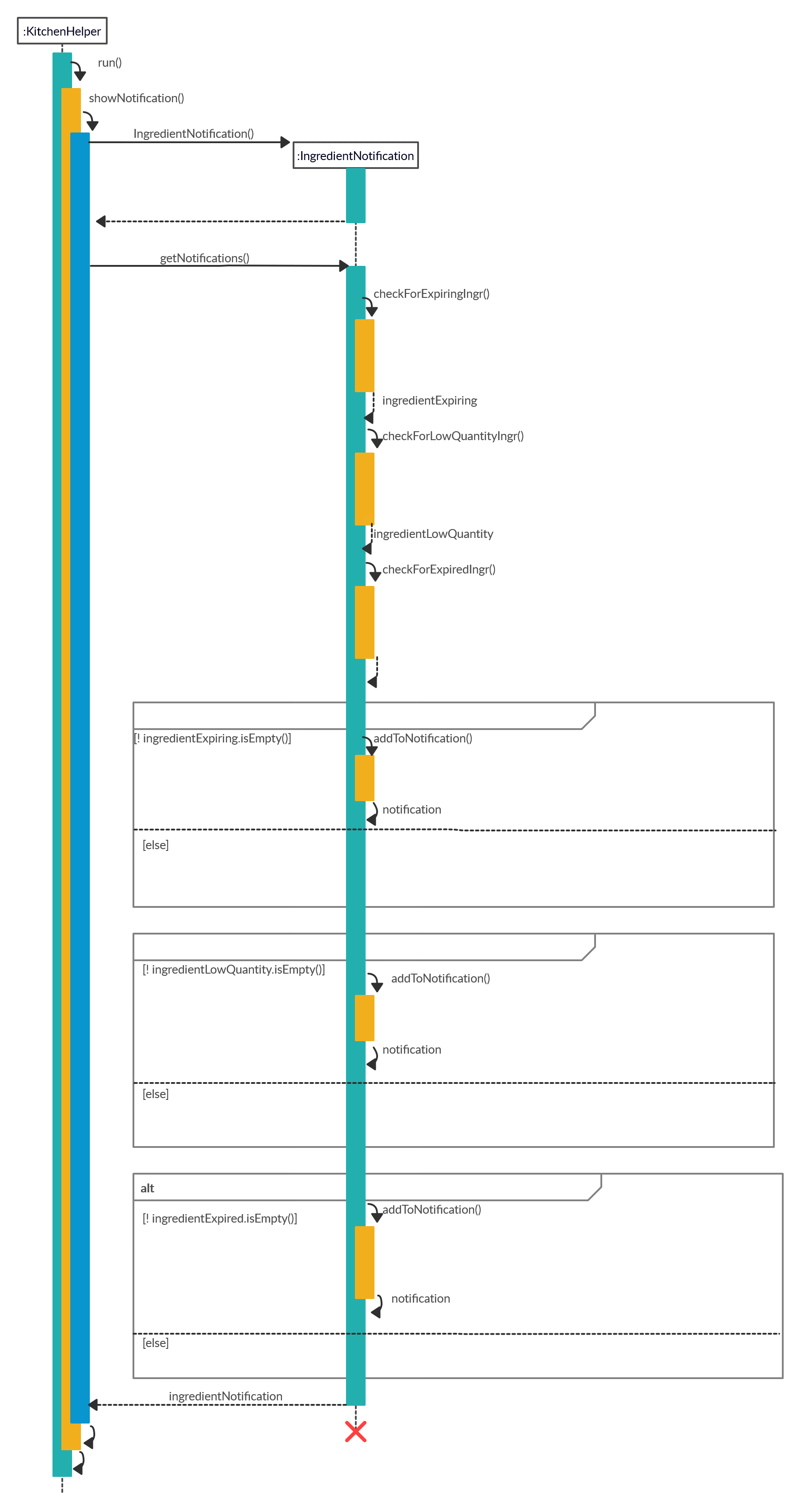
The following steps explained sequence diagram for showNotification method:
- The user starts
KitchenHelper. KitchenHelpercallsshowNotification().KitchenHelper#IngredientNotificationobject is created when the methodIngredientNotification#getNotifications(ingredientList)is called.- Result from
IngredientNotification#checkForExpiringIngr(ingredientList),IngredientNotification#checkForLowQuantityIngr,IngredientNotification#checkForExpiredIngrwill be combined.IngredientNotification#checkForExpiringIngr(ingredientList)checks for ingredients that is going to expire in 3 days.IngredientNotification#checkForLowQuantityIngrchecks for ingredients that has quantity of 5 or lower.IngredientNotification#checkForExpiredIngrchecks for ingredients that is expired.
IngredientNotification#getNotifications(ingredientList)returns result toKitchenHelper#ingredientNotificationand displays.
Design considerations:
Aspects: How showNotification executes:
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Create a function to compile results from the three different methods,
| Pros | 1. Decreases the need to indicate three lines of code to call out the three different methods. |
| Cons | 1. Developer have to go into IngredientNotification#getNotifications(ingredientList) to find out what function |
- Alternative 2: Create three different methods in
KitchenHelper.java
| Pros | 1. Clear indication what the method is doing |
| Cons | 1. Not very ‘OOP’ like |
4.2. Recipe-related Features
4.2.1. Addition of recipe
Users can add a new recipe to the application where there must be at least one or more ingredients. The failure to do so will trigger an exception where the user will be notified of an invalid command and the syntax of the addition of recipe will be displayed.
It is important that the name of the new recipe has not appeared in the list of recipes in the application.
Implementation
When the user attempts to create a new recipe, the AddRecipeCommand, Parser and Recipe class will be accessed and the following sequence of actions are called to create a recipe object:
- User executes
addrecipe /n Chicken Salad /i Chicken Breast:2:meat, Lettuce:4:vegetable- A
Uiobject will be created and callsUi#getUserCommand() - Input will be parsed in
Parser#parseUserCommand()and identified with the keywordaddrecipe.
- A
- Parsing of user input and creation of command object
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string into a suitable format for the addition of
recipeobject inParser#prepareAddRecipe(). - A
AddRecipeCommandobject will be created and callsAddRecipeCommand#setAttributesOfCmd()to set the contents of the command into reader friendly formats.
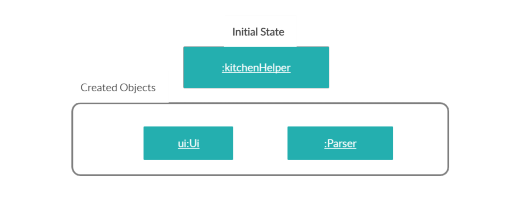
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string into a suitable format for the addition of
- Executing Command
- The newly created object will call
AddRecipeCommand#execute()which starts the process of adding a recipe, thus callingRecipe#AddRecipe(). - A
Recipeobject will be created with its name that was parsed in step 2. - An additional step is included where a check for an existing recipe with the same name is conducted with
AddRecipeCommand#checkIfRecipeExist(). AKitchenHelperExceptionexception will be triggered when there is an existing recipe.
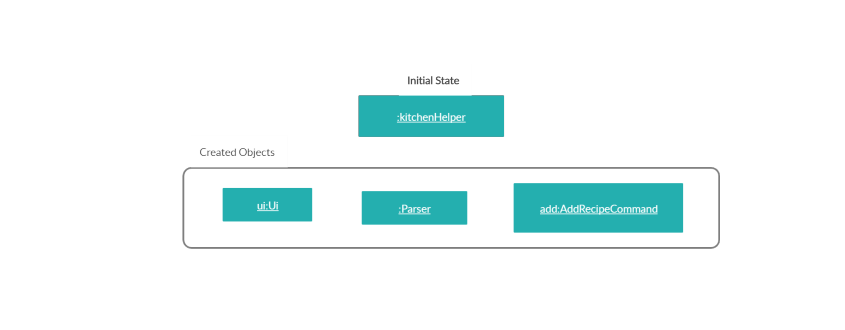
- The newly created object will call
-
Ingredients parsed in step 2 will be added to the newly created recipe according to their category through the calling ofRecipe#addIngredientsToRecipe().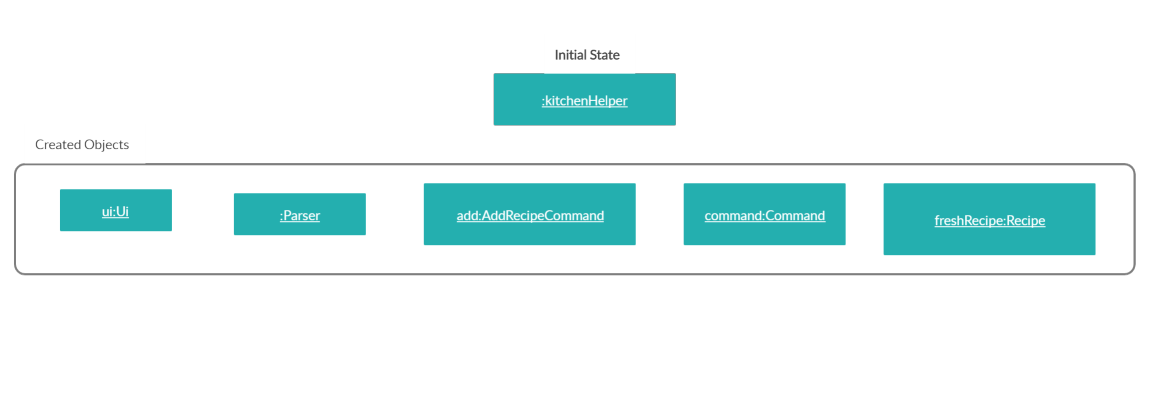
All description and warnings to the user utilises the UI class, which controls the printing of the text on the console.
The following sequence diagram shows how the addrecipe command works
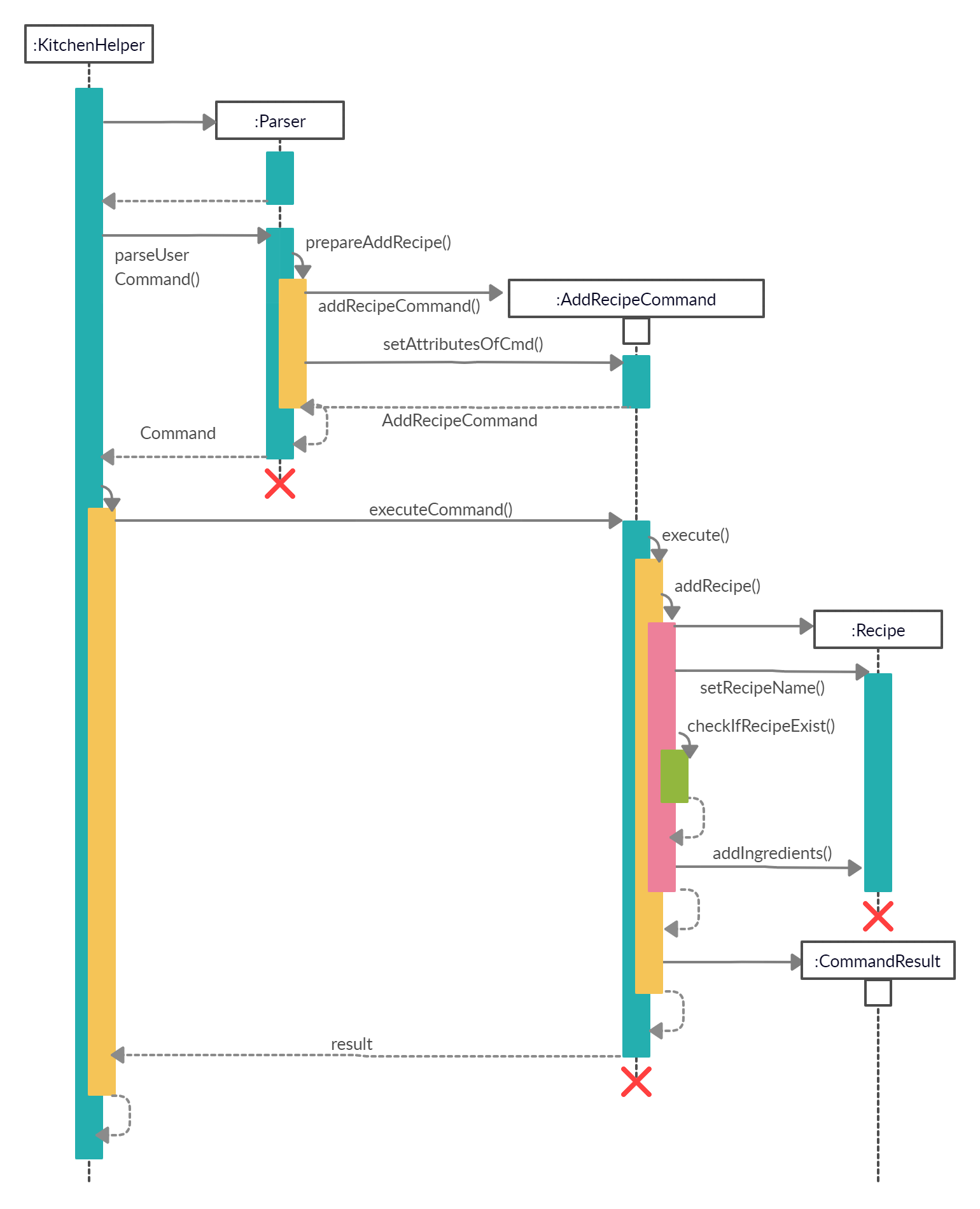
Design Considerations
Aspect: Parsing of the user’s input command
Alternative 1 (current choice): The key parameters that are required are divided by the delimiter of ‘/’ followed by a specific letter. (i.e. /i)
| Pros | User would be able to have strings that may contain spaces (i.e. /n Chicken Salad /i Breast meat:2:meat) |
| Cons | The order of delimiters needs to be standardized, users will not be able to re-order the delimiters. |
Alternative 2: Multiple prompts for user’s input of a recipe name and ingredient(s)
| Pros | Users would not have to make sure that their command is syntactically right |
| Cons | The constant prompting could subject the application to a negative experience in the difficulty to use the commands. |
Alternative 3: User’s command are divided by space
| Pros | The parsing can be easily done by calling Java built-in function .split() |
| Cons | Values for each variable cannot contain spaces which makes the application restrictive. |
4.2.2. List all/ specific recipe(s)
The list feature allows showing details of a particular recipe created by the user. All ingredients added into the recipe will be shown in a sorted order and shown by categories. The function will require valid string of a integer or all to be added as a parameter. Failure to do so will trigger an exception where the user will be notified of an invalid command and the syntax of the listing of the recipe will be displayed.
Implementation
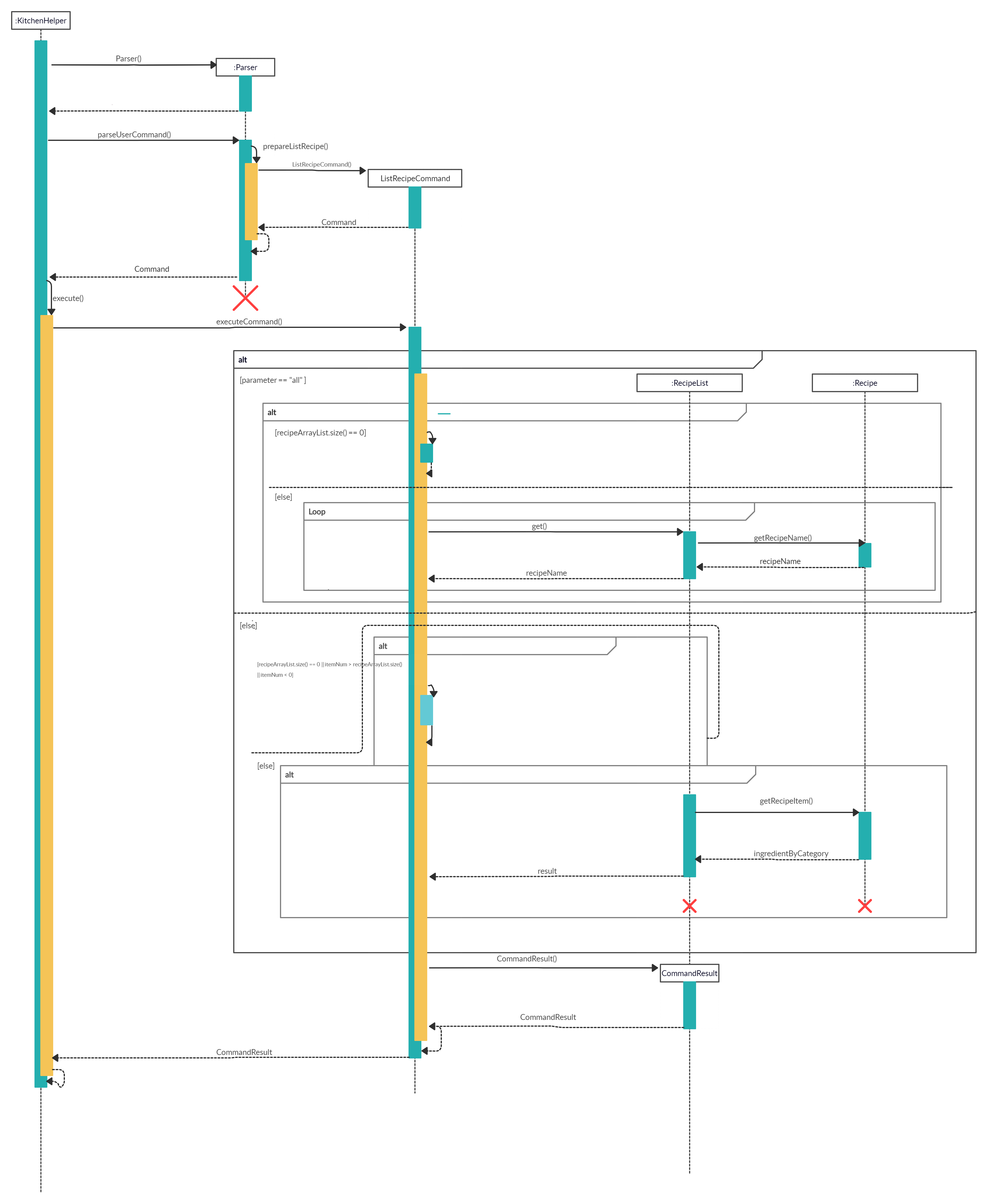
When the user attempts to list the details of a particular recipe, the listRecipeCommand, ‘Parser’ and Recipe class will be accessed and the following sequence of actions are called to list details of a particular recipe object:
The following image below shows the sequence of steps for step 1 and 2:
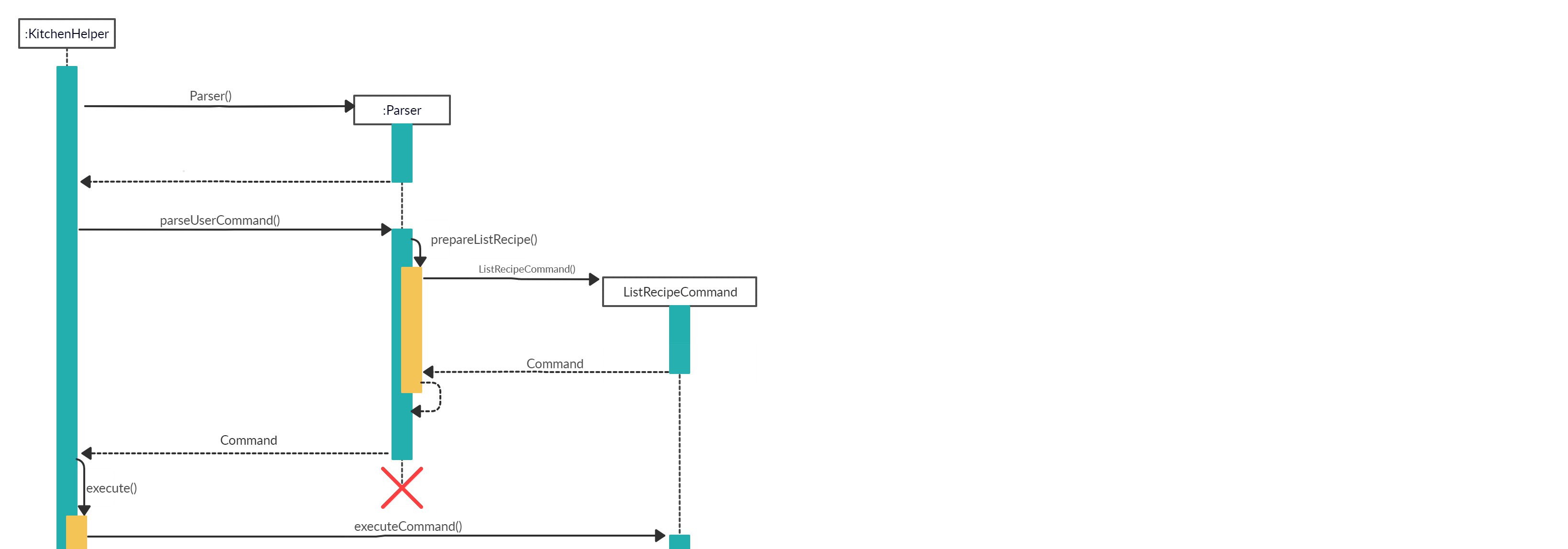
- User executes
listrecipe 1- A
Uiobject will be created and callsUi#getUserCommand() - Input will be parsed in
Command#parseUserCommand()and identified with the keywordlistrecipe.
- A
- Parsing of user input and creation of command object
2.This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string into a suitable format for the listing of
recipeobject inCommand#prepareListRecipe().- A
ListRecipeCommandobject will be created.
- A
-
Executing Command The following image below shows the sequence for the next steps:
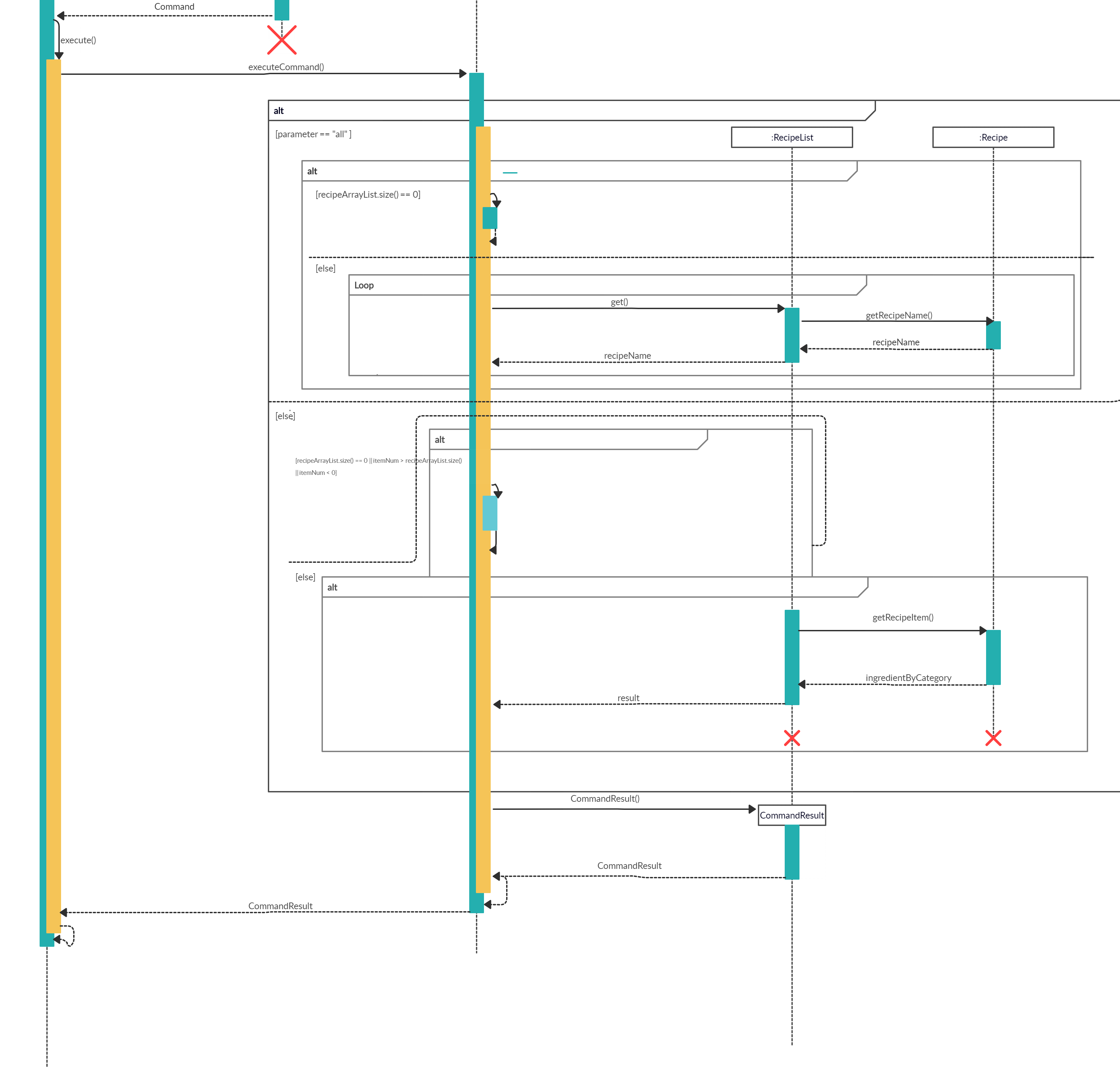
- The newly created object will call
ListRecipeCommand#executewhich starts the process of listing a particular recipe’s details, thus, callingListRecipeCommand#listRecipe(). - The existing recipeList arraylist and the item number of the chosen recipe will be passed through to the
ListRecipeCommand#listRecipe(). - The function will find if the item number is valid and contains details of the recipe, thus, creates a CommandResult storing the details of the particular recipe.
- The newly created object will call
- The details will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result). The following shows the full sequence diagram for this command:
Design Considerations
Aspect: Finding the recipe requested by the user.
Alternative 1: Looping through the whole recipeList arraylist to find the recipe requested by the user.
| Pros | The program will be able to locate the recipe accurately. |
| Cons | This method will be slow when facing a huge amount of data in the arraylist as the program may have to go through every single item in the arraylist. |
Alternative 2 (current choice): Using arrayList.get(item) to get the recipe requested by the user.
| Pros | Users would be able to get the details of the particular recipe accurately and fast. |
| Cons | Without proper checks done before running the command, it will result in error if the number indicated by the user exceeds the arraylist / does not exist in the arraylist. |
4.2.3. Cooking of recipe
The feature allows the user to cook a recipe if there are sufficient ingredients. The user will also indicate how many pax this recipe would be cooked for.
Implementation
When the user attempts to cook Chicken Salad recipe from Kitchen Helper, the Kitchen Helper, Parser and cookRecipeCommand class will be called upon. The following sequence of steps will then occur:
-
The user keyed in
cookrecipe /n Chicken Salad /p 1.- A
UIobject will be created and it will callUI#getUserCommand()method to take in the input that the user has keyed in. - A
Stringobject will be returned and saved into theuserCommandInputvariable inKitchen Helper. - The variable
userCommandInputis being parsed into theParserclass as an argument for this methodParser#parseUserCommand().

- A
-
The command inserted by the user is being parsed into the
Parserand a newCommandobject is being created.- The variable
userCommandInputwill be identified ascookrecipein theParser#parseUserCommand().TheParser#prepareCookRecipe()is being called to prepare theuserCommandInputstring to create aCookRecipeCommandobject.
- The variable
-
The command is now being executed.
- The
CookRecipeCommand#execute()will be called. - The
CookRecipeCommand#cookRecipe()is called and it checks whether the recipe inputted by the user exists by calling theCookRecipeCommand#checkIfRecipeExists()method. - If recipe exists, the
CookRecipeCommand#checkIfRecipeExists()method will return the index of the recipe, else it will return a number that is bigger than the size ofrecipelist. In this case, the recipeChicken Saladexists, so it will return the index of the recipe - Next, it is to check if there are sufficient non-expiring ingredients to be deducted from the ingredients’ inventory to cater for the number of pax for the specific recipe by calling
CookRecipeCommand#checkForSufficientIngredients()andCookRecipeCommand#checkNotExpiredIngredientQty()which their results are saved intosufficientIngrandsuffButLessExpiredIngrboolean values respectively.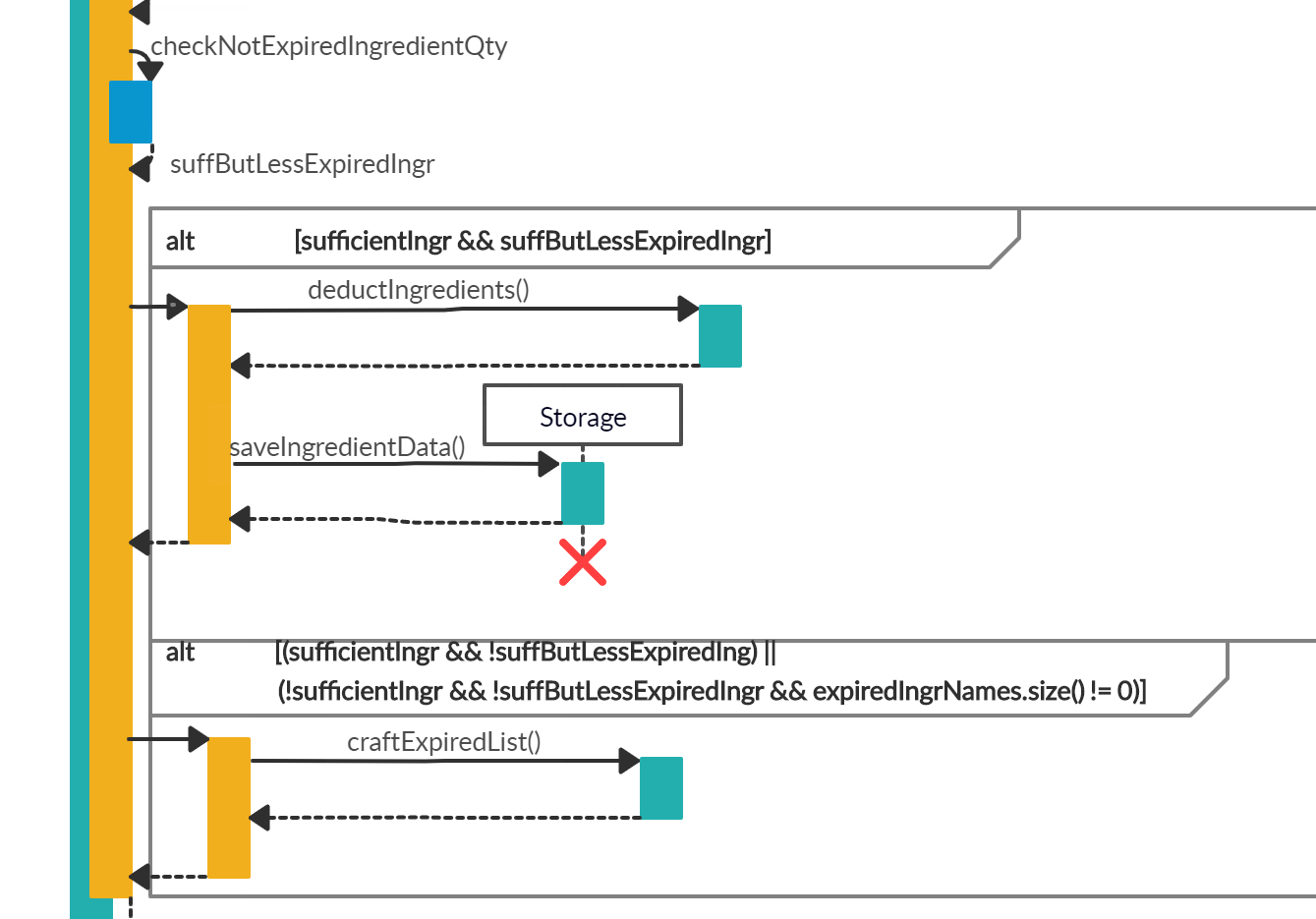
- With respect to the point 4 above, the following cases may happen and has been summarised at the image above:
- Case 1: If both
sufficientIngrandsuffButLessExpiredIngrreturn trueCookRecipeCommand#deductIngredients()will be called to deduct the ingredients in the ingredients’ inventory.- Then,
Storage#saveIngredientData()will be called to save the currentingredientsListinto an output file.
- Case 2: If
sufficientIngrreturns true butsuffButLessExpiredIngrreturns false or bothsufficientIngrandsuffButLessExpiredIngrreturn false and the size ofexpiredIngrNamesis not zeroCookRecipeCommand#craftExpiredList()will be called to craft the list of expired ingredients which will be returned to tell the users the ingredients that are expired.
- Case 1: If both
The following image shows the state diagram for the command execution:
- The
-
The details will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
The following shows the full sequence diagram for this command:
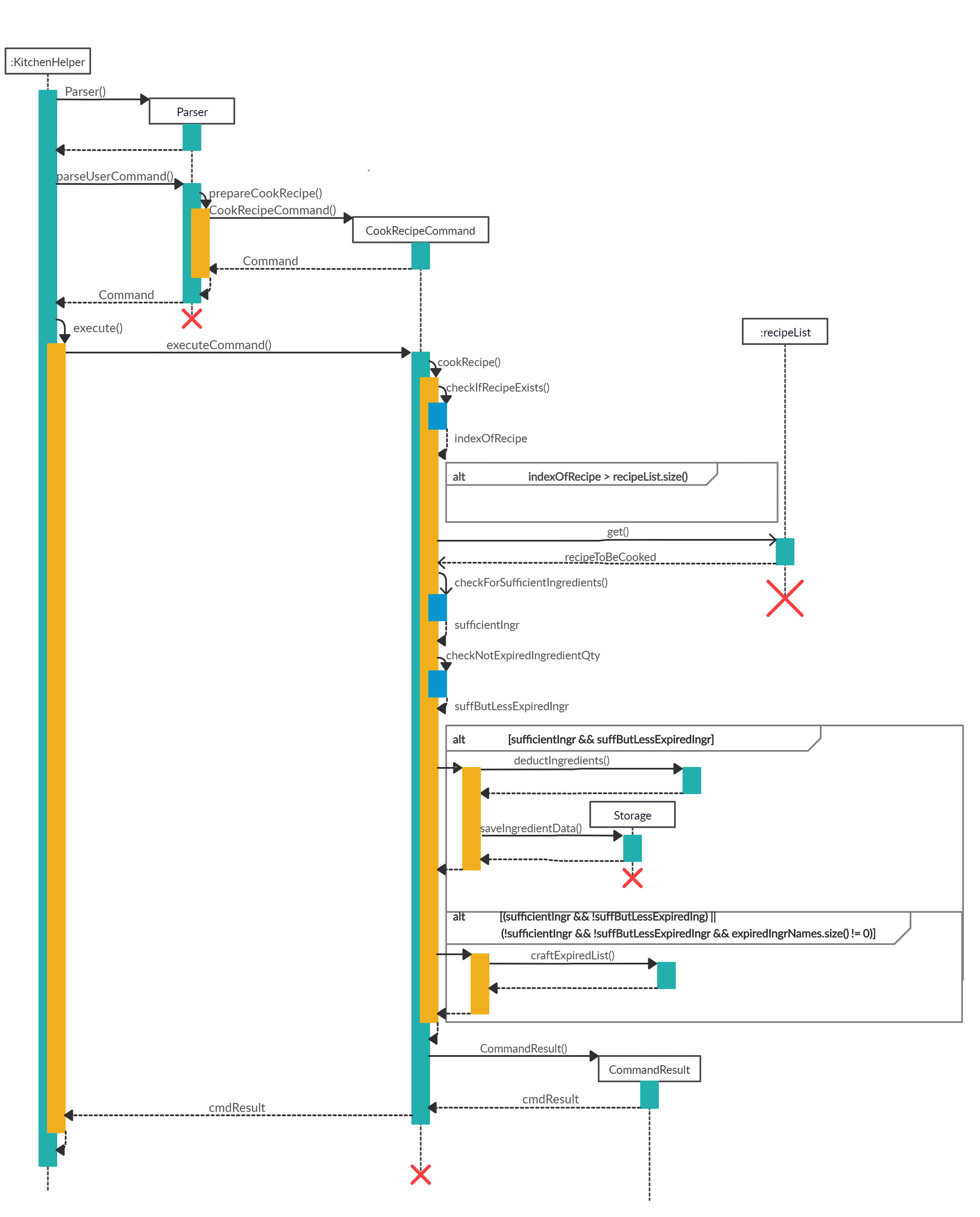
Other than reducing the quantity of ingredients if the recipe can be cooked successfully, CookRecipeCommand has an additional feature that is linked to Display Expenditure which will add the total cost of cooking this recipe into the total expenditure.
Design considerations
Aspect: Preparing the deduction of ingredients when cooking a recipe
Alternative 1 (current choice): Checks for existence of recipe, existence of ingredients for the specified recipe and sufficiency of ingredients
| Pros | Minimizes erroneous deduction of insufficient and nonexistent ingredients |
| Cons | Additional computation and overhead |
Alternative 2: Deductions are to be made to existing and available ingredients and users are notified when there are insufficient ingredients
| Pros | Lesser overhead as there is lesser checks to be done |
| Cons | Hidden bugs and exceptions have to be well-covered to ensure that the deduction would be of the right value |
Aspect: Searching for the corresponding ingredients of a recipe/ Searching through list of recipes to check for existence of recipe Alternative 1 (current choice): Linear search, iterate through the arraylist of ingredients/ recipes and checking
| Pros | Lesser use of complex data structure will save memory |
| Cons | Not optimal as search will be O(n), larger amount of data may take a longer time |
Alternative 2: building an index on the first letter of the recipe name
| Pros | More efficient search as pool of search space would be significantly smaller |
| Cons | Needs to be constantly maintained which incurs overhead. |
4.2.4. Delete a specific recipe
The deletion feature for specific recipes allows the user to delete recipes either by the name or index of the recipe.
Implementation
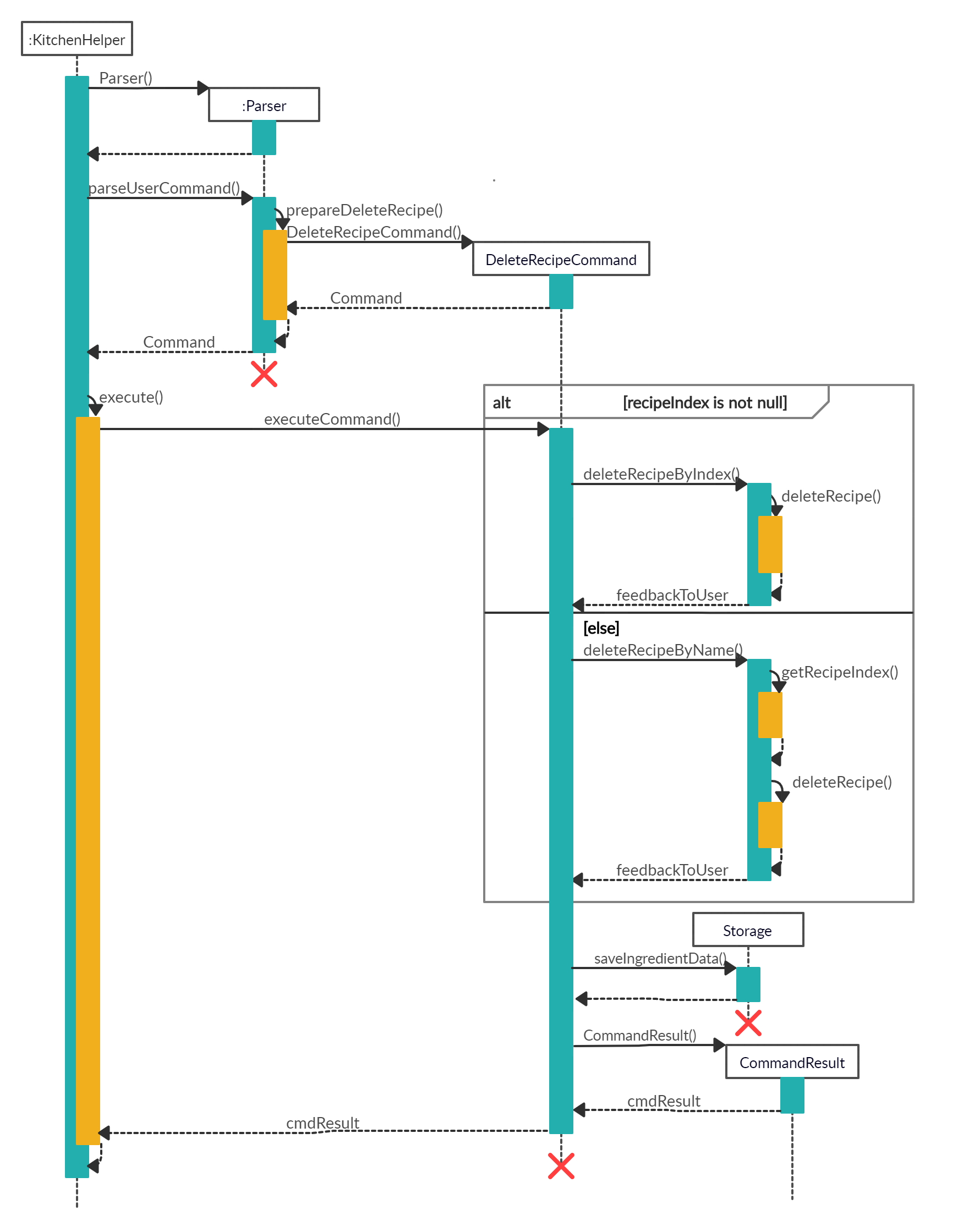
When the user attempts to delete the Chicken Rice recipe from Kitchen Helper, the Kitchen Helper, Parser and DeleteRecipeCommand class will be called upon. The following sequence of steps will then occur:
-
The user keyed in
deleterecipe /n Chicken Rice.- A
UIobject will be created and it will callUI#getUserCommand()method to take in the input that the user has keyed in. - A
Stringobject will be returned and saved into theuserCommandInputvariable inKitchen Helper. - The variable
userCommandInputis being parsed into theParserclass as an argument for this methodParser#parseUserCommand().

- A
-
The command inserted by the user is being parsed into the
Parserand a newCommandobject is being created.- The variable
userCommandInputwill be identified asdeleterecipein theParser#parseUserCommand().TheParser#prepareDeleteRecipe()is being called to prepare theuserCommandInputstring to create aDeleteRecipeCommandobject.
- The variable
-
The command is now being executed.
- The
DeleteRecipeCommand#execute()will be called. - As this is a deletion by recipe name, the
recipeIndexvariable is set as null. As the variable is null,DeleteRecipeCommand#deleteRecipeByName()will be called. - Next, the
DeleteRecipeCommand#getRecipeIndex()to get the index based on the recipe name that the user has inputted. With the given index,DeleteRecipeCommand#deleteRecipe()will be called to delete the recipe. - Lastly, a String called
feedbackToUserwill be returned to the user to inform the user of the outcome of the command.
The following image shows the state diagram for the command execution:
- The
-
The details will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
The following shows the full sequence diagram for this command:
Design Considerations
- Aspect 1: How is the
DeleteRecipeCommandinitialise.
-
Alternative 1 (Current Choice): Usage of 2 constructors
Pros This gives us more flexibility on what object can be created with different variables since there are two methods of recipe deletion. Cons There is an overload of constructors. -
Alternative 2: Usage of 1 constructor
Pros The Parser can call for one main default constructor. Cons The single constructor will need to deal with 2 different methods of deletion, causing the constructor to have more than one purpose.
In the end, for
aspect 1, we have chosenalternative 1as there are two different types of deletion, it would be simpler and increase cohesion as it is more easier to express these constructors’ functionality at a higher level. -
- Aspect 2: Deletion by both index and name for recipes
-
Alternative 1: Deletion by index only
Pros A very specific recipe can be deleted. Cons Users will not be able to delete the recipe by name. -
Alternative 2 (Current Choice): Deletion by both index and name
Pros Users will be able to delete by recipe’s name and index. As the recipe names are specific, it will be easier to get the recipe from list of recipe by getting the index from the recipe name given or the index given by the user. Cons There may be more overhead as there is a need to find the index of the recipe if the user has given the recipe name for deletion.
In the end, for
aspect 2, we have chosenalternative 2which is to delete by index and name for recipes as the recipe names are unique when they are added, hence the users will be able to delete that specific recipe. -
4.2.5. Search for recipe based on keyword(s)
The search for recipe feature allows the user to find recipes using a keyword in the recipe’s list.
For example, searchrecipe Chicken will find all recipes that contain Chicken.
Implementation
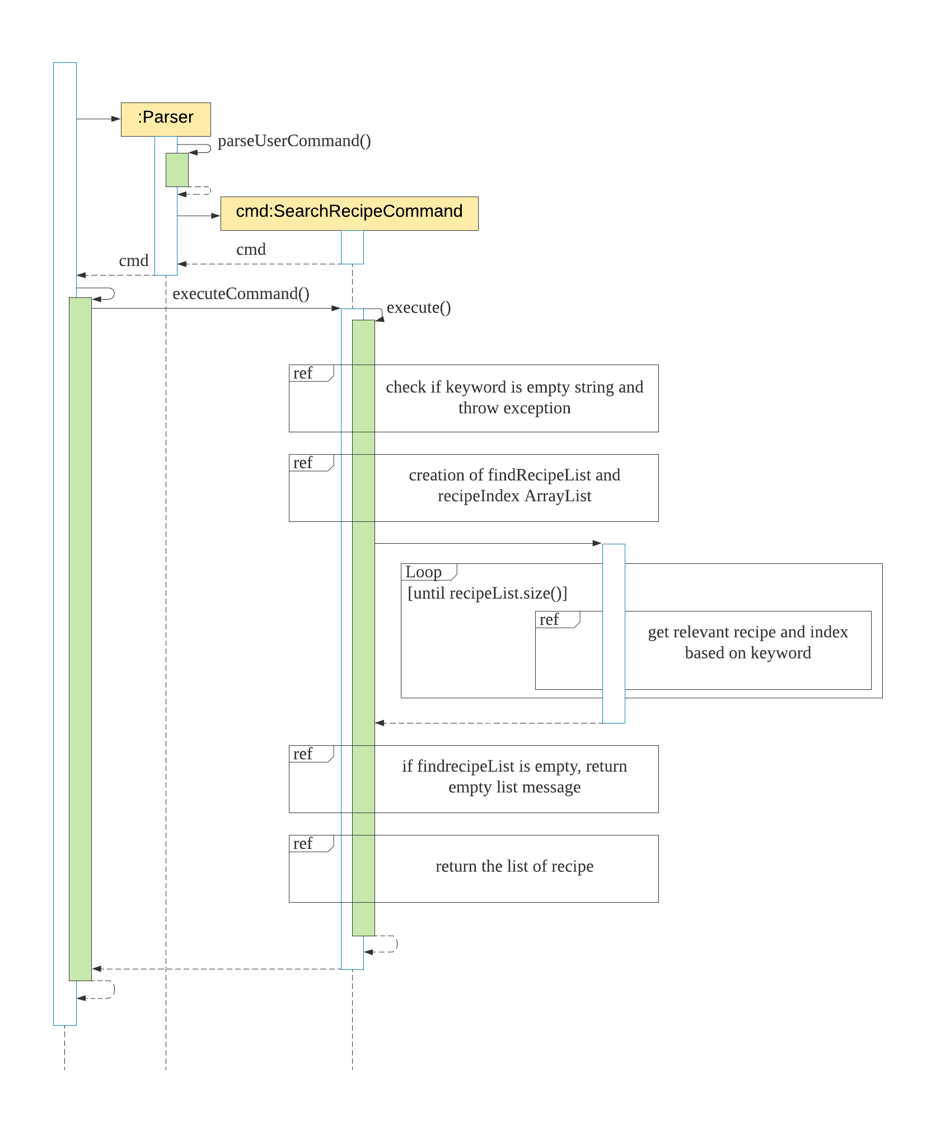
The following steps explained sequence diagram for searchrecipe command:
- The user enters
searchrecipe Chicken. KitchenHelpercallsParser#parseUserCommand().SearchRecipeCommandobject is created with the keyword passed in.KitchenHelpercalls it own methodexecuteCommand()to execute the method inSearchRecipeCommand#execute().- On
SearchRecipeCommand#execute(), display the list of recipe’s name that matches the keyword.
Design considerations:
Aspects: How searchrecipe executes:
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Find if the keyword is part of the substring of the recipe’s name and returns the recipe’s name and the index of recipe in the recipe’s list.
| Pros | 1. Easy to find similar recipe by their name. |
| Cons | 1. Only shows the different recipe that contains the keyword. |
- Alternative 2: Find the keyword within the recipe’s ingredient.
| Pros | 1. More accurate searching of the recipe that uses the ingredients. |
| Cons | 1. Could be more memory intensive to find if the list is huge. |
4.3. Chore-related Features
4.3.1. Addition of chore
The feature for addition of chores allows the user to add chores to a list to keep track of their completion. The deadline of the chore can be a String or Date object. The status completion of a chore is always undone when it is created.
Implementation
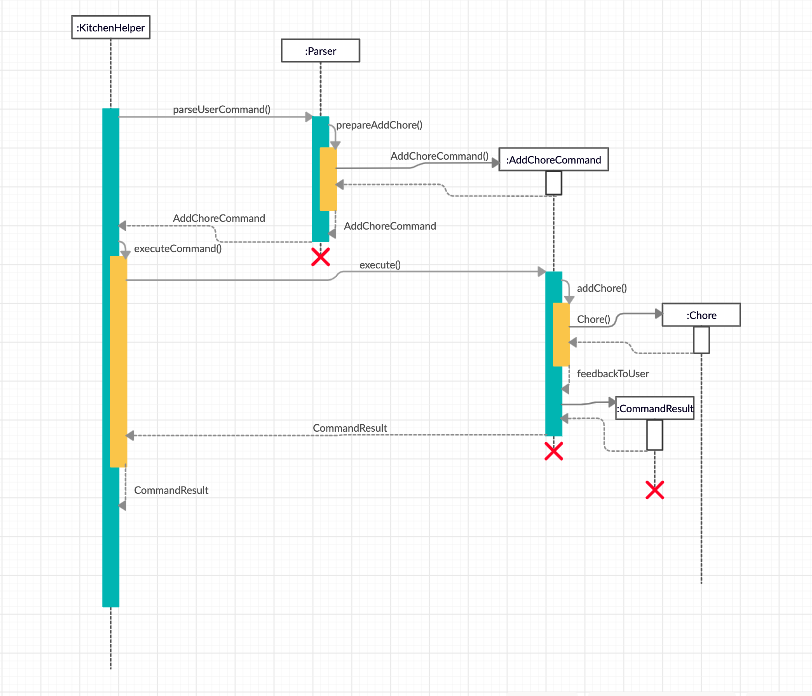
When the user attempts to add a chore buy groceries with deadline 13/04/2020 09:45, the Kitchen Helper, Parser and AddChoreCommand class will be called upon. The following sequence of steps will then occur:
-
The user keyed in
addchore buy groceries /by 13/04/2020 09:45.- A
UIobject will be created and callsUI#getUserCommand(). - Input will be parsed in
Parser#parseUserCommand()and identified with the keywordaddchore.
- A
- Parsing of user input and creation of command object
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string into a suitable format for the addition of
choreobject inParser#prepareAddChore(). - A
AddChoreCommandobject will be created with parametersbuy groceriesas String description and13/04/2020 09:45as Date deadline.
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string into a suitable format for the addition of
- Executing Command
- The newly created object will call
AddChoreCommand#execute()which starts the process of adding a chore, thus callingAddChoreCommand#addChore(). - A
Choreobject will be created with the description and deadline that was parsed in step 2. Since the String deadline value is null, the deadline of theChorewill be aDateobject. - The
Chorewill be added to thechoreList. - Then,
Storage#saveChoreData()will be called to save the currentchoreListinto an output file. - Lastly, a String called
feedbackToUsercontaining the outcome of the command will be returned toKitchenHelper.
- The newly created object will call
- The outcome of the command will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
The following sequence diagram shows how the AddChoreCommand works
Design considerations:
- Alternative 1(current implementation): The
Chorewith different deadline types is created by constructor overloading.
| Pros | It is neater and more OOP. It indicates that both Chores with different deadline types have the same object function, but just take in different parameters. |
| Cons | The need to maintain both a String deadline and Date deadline variable within the Chore object even though one of them is not used. |
- Alternative 2: Creation of
Choreobject by setting up variables using if-else loop.
| Pros | More basic implementation. |
| Cons | Less OOP and does not make it obvious that deadline is an essential attribute of a Chore object that has two type signatures to choose from. |
4.3.2. List all chores
The feature to list chores allows the user to view the chores currently in the choreList and their completion statuses.
Implementation
When the user attempts to list chores, the Kitchen Helper, Parser and ListChoreCommand class will be called upon. The following sequence of steps will then occur:
- The user keyed in
listchore.- A
UIobject will be created and callsUI#getUserCommand(). - Input will be parsed in
Parser#parseUserCommand()and identified with the keywordlistchore.
- A
- Parsing of user input and creation of command object
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string in
Parser#prepareListChore()to ensure the parameters are empty, or an exception will be thrown. - The
ListChoreCommandobject will be created.
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string in
- Executing Command
- The newly created object will call
ListChoreCommand#execute()which starts the process of displaying all the chores, thus callingListChoreCommand#listChore(). - The
choreListwill be looped through, displaying eachChorein String format and its corresponding position in the list. - Lastly, a String called
feedbackToUsercontaining the displayed list of chores will be returned toKitchenHelper.
- The newly created object will call
- The displayed list of chores will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
Design considerations:
- Alternative 1(current implementation): Using for-loop to loop through the
ChoreArrayList.
| Pros | It is easier to retrieve the position of each Chore in the list, just by looking at the iterator value. |
| Cons | More basic implementation. |
- Alternative 2: Using ListIterator to loop through the
ChoreArrayList.
| Pros | Makes use of the Java Collection framework. |
| Cons | Requires another counter or variable to keep track of Chore position in the list. |
4.3.3. Delete a specific chore
The feature for deletion of chores allows the user to remove the chore specified by the index in the list.
Implementation
When the user attempts to delete a chore by its index, the Kitchen Helper, Parser and DeleteChoreCommand class will be called upon. The following sequence of steps will then occur:
- The user keyed in
deletechore 1.- A
UIobject will be created and callsUI#getUserCommand(). - Input will be parsed in
Parser#parseUserCommand()and identified with the keyworddeletechore.
- A
- Parsing of user input and creation of command object
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string for the deletion of
choreobject inParser#prepareDeleteChore()which ensures the parameter is a single number, or an exception will be thrown. - If an exception is caught, an InvalidCommand will be created. Otherwise, a
DeleteChoreCommandobject will be created with parameters1as the index to delete.
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string for the deletion of
- Executing Command
- The newly created object will call
DeleteChoreCommand#execute()which starts the process of deleting a chore, thus callingDeleteChoreCommand#deleteChore(). - The index is checked to be an index within the
choreList, then theChorespecified by the index in thechoreListis removed. - Then,
Storage#saveChoreData()will be called to save the currentchoreListinto an output file. - Lastly, a String called
feedbackToUsercontaining the outcome of the command will be returned toKitchenHelper.
- The newly created object will call
- The outcome of the command will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
Design considerations:
- Alternative 1(current implementation): Delete
Choreby specifying index ofChoreinchoreList.
| Pros | Quick and easy deletion by using choreList.get() to retrieve Chore to delete. |
| Cons | Lesser alternatives for the user and user would have to identify the index first by executing listchore to get index of Chore in choreList. |
- Alternative 2: Delete
Choreby specifyingChoredescription or keywords inChoredescription.
| Pros | More alternatives for user. |
| Cons | 1. Extra overhead required to search through entire choreList to identify Chore with similar description. 2. Possible accidental deletion of wrong Chore with identical descriptions or keywords. 3. More troublesome for the user to type out exact description of Chore. |
4.3.4. Search for chore based on keyword(s)
The search for chore feature allows the user to find chores using a keyword in the chore’s list.
For example, searchchore groceries will find all chores that contain groceries.
Implementation
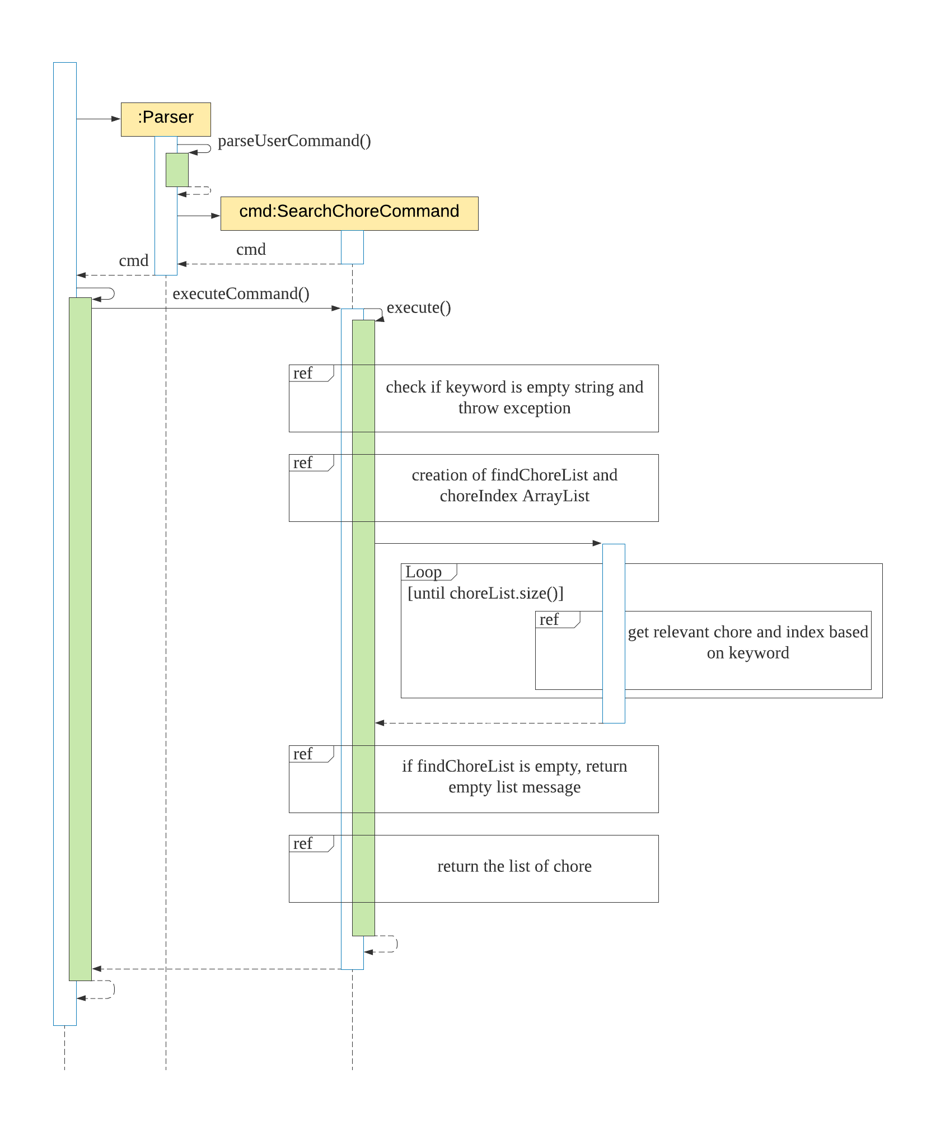
The following steps explained sequence diagram for searchchore command:
- The user enters
searchchore groceries. KitchenHelpercallsParser#parseUserCommand().SearchChoreCommandobject is created with the keyword passed in.KitchenHelpercalls it own methodexecuteCommand()to execute the method inSearchChoreCommand#execute().- On
SearchChoreCommand#execute(), display the list of chore that matches the keyword.
Design considerations:
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Find if the keyword is part of the substring of the chore,
[x] buy groceries (by: Tuesday 12pm).
| Pros | 1. Easily to find by any attributes such as description and date. |
| Cons | 1. Searching buy groceries [x] will fail to show any matching result. |
- Alternative 2: Take in all the predicates given by the user and find using the predicates as a keyword
| Pros | 1. More accurate searching of the chore is available for the user.. |
| Cons | 1. Requires users to enter more precise predicate keywords which could be more inconvenient. |
4.3.5. Mark chore as done
The feature for marking of chore as done allows the user to change the completion status of the chore specified by the index in the list to done.
Implementation
When the user attempts to mark a chore as done, the Kitchen Helper, Parser and DoneCommand class will be called upon. The following sequence of steps will then occur:
- The user keyed in
done 1.- A
UIobject will be created and callsUI#getUserCommand(). - Input will be parsed in
Parser#parseUserCommand()and identified with the keyworddone.
- A
- Parsing of user input and creation of command object
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string for the checking of
choreobject inParser#prepareDoneChore()which ensures the parameter is a single number, or an exception will be thrown. - If an exception is caught, an InvalidCommand will be created. Otherwise, a
DoneCommandobject will be created with parameters1as the index to check.
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string for the checking of
- Executing Command
- The newly created object will call
DoneCommand#execute()which starts the process of marking a chore as done, thus callingDoneChoreCommand#markChoreDone(). - The index is checked to be an index within the
choreListand completion status of theChorespecified by the index is checked to be undone. Otherwise, an exception will be thrown. - The Chore is then marked as done.
- Then,
Storage#saveChoreData()will be called to save the currentchoreListinto an output file. - Lastly, a String called
feedbackToUsercontaining the outcome of the command will be returned toKitchenHelper.
- The newly created object will call
- The outcome of the command will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
Design considerations:
- Similar to DeleteChoreCommand.
4.3.6. Notification for chores warning
The notification for chores warning runs every time the program starts. It checks the choreList for Chores that are already overdue or have deadlines approaching in 3 days.
For example, take cake out of oven is overdue since 11/04/2020 15:30. Deadlines of Chores specified in String will not trigger notification warnings.
Implementation
- The user starts
KitchenHelperandKitchenHelper#runis called. KitchenHelpercallsshowNotification().ChoreNotificationobject is created andChoreNotification#getNotifications(choreList)is called.- The results from
ChoreNotification#hasDateAsDeadline,ChoreNotification#isOverdueandChoreNotification#isApproachingDeadlinewill be combined.ChoreNotification#hasDateAsDeadlinechecks forChoresthat have Date object type deadline.ChoreNotification#isOverduechecks forChoresthat have exceeded their deadline.ChoreNotification#isApproachingDeadlinechecks forChoresthat have deadlines upcoming in the next 3 days.
ChoreNotification#getNotifications(choreList)returns the String result containing the notifications toKitchenHelperand displays.
Design considerations:
Aspects: How showNotification executes:
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Create a function that creates a ChoreNotification class object that gathers the notifications to print.
| Pros | More OOP as there is a specific class handling the sole function of notification display. |
| Cons | Developer has to go into ChoreNotification class to find out how to notifications are gathered. |
- Alternative 2: Create the methods to gather notifications in
KitchenHelper.java
| Pros | More basic implementation. |
| Cons | Less OOP and the KitchenHelper main class will be overpopulated with methods that do not concern the overall running of the application. |
4.4. Storage
4.4.1. Select files to load from and save to
The select files to load from and save to feature allows the user to choose an option to either load their data from the normal or restore mode. The normal mode will load Kitchen Helper from the main storage files which store the data from the last used session of the user, providing the most recent representation of their inventory.
On the other hand, the restore mode will load Kitchen Helper from the backup storage files which store the version of data manually saved from the user’s last usage of the save command. The restore mode gives users access to the backup storage files, however, users will have to use the save command to update the backup storage files.
Any subsequent changes made to the program data will be saved into the main storage files regardless of initial load options. To save a backup of the current session, the user will have to use the save current state function with the save command (see section 4.4.2)4.4.2. Save current state.
Implementation
- For instance, if the User selects to load files from auto-save mode, User executes
1- A
Uiobject will be created and callsUi#getUserChoice()and returns StringUserChoice. - The
Uiobject then callsUi#validUserChoice()withUserChoiceas the parameter. IfUserChoiceis invalid,Ui#validUserChoice()will callUi#askForReInput().
- A
-
Creation of storage object
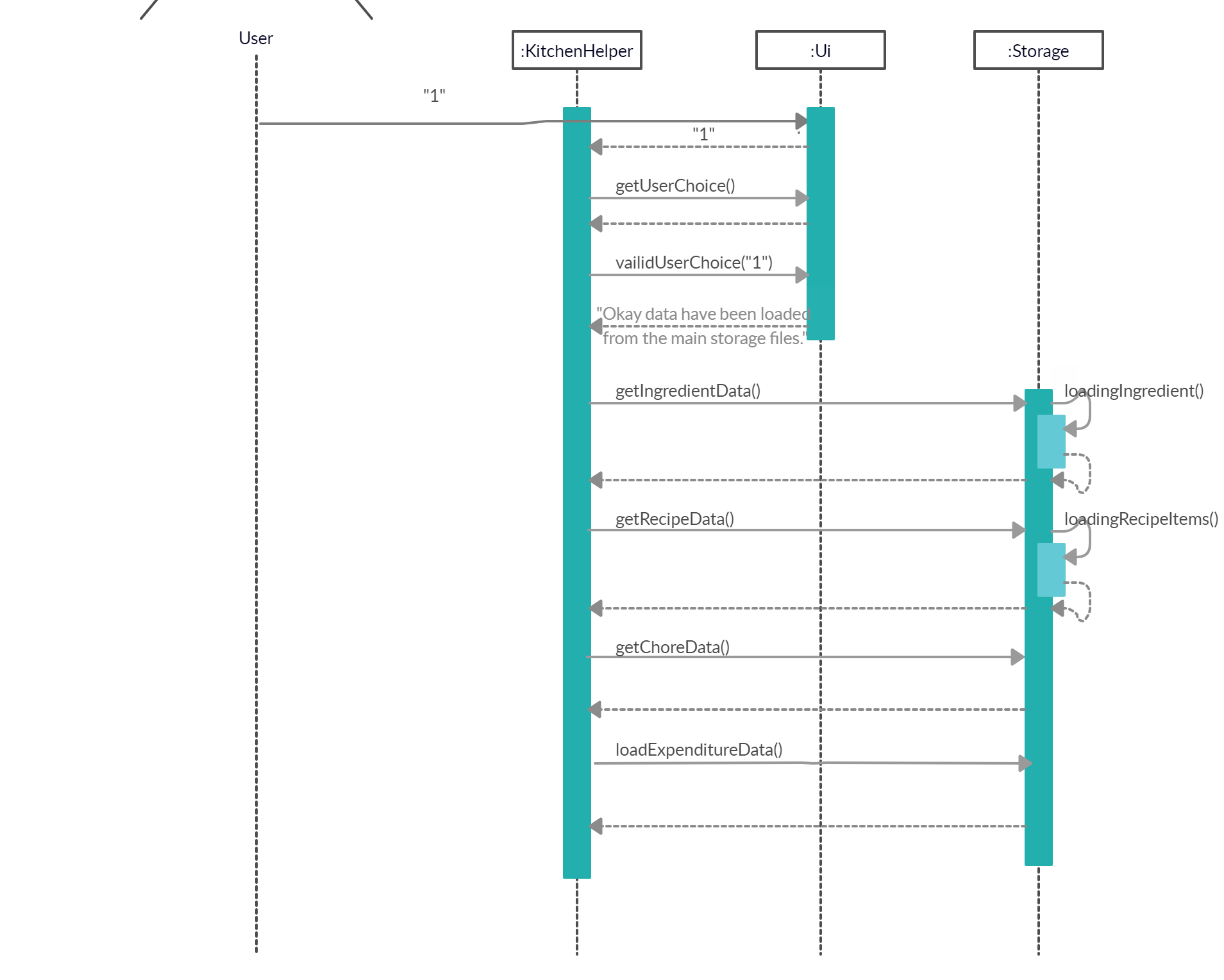
Ingredient data:
- A
Storageobject will be created and callsStorage#getIngredientData()to load and parse the contents of ingredient save file into a newly createdingredientList ArrayList<Ingredient>. Storage#getIngredientData()will callStorage#loadingIngredient()to createIngredientobjects based on the category type of ingredients in theingredientList.
Recipe data:
- A
Storageobject will be created and callsStorage#getRecipeData()to load and parse the contents of recipe save file into a newly createdrecipeList ArrayList<Recipe>. Storage#getRecipeData()will create aRecipeobject andrecipeItems ArrayList<Ingredient>. It then callsStorage#loadingRecipeItems()to createIngredientobjects based on the category type of ingredients in each recipe into therecipeItems. Every ` recipeItemsof each recipe will then be added intorecipeList`.
Chore data:
- A
Storageobject will be created and callsStorage#getChoreData()to load and parse the contents of chore save file into a newly createdchoreList ArrayList<Chore>.
Expenditure data:
Storage#loadExpenditureData()is called to load and parse the contents of expenditure save file and creates an instance ofExpenditure.
- A
All description and warnings to the user utilises the UI class, which controls the printing of the text on the console.
The sequence diagram below summarizes how loading data works:
Design considerations:
Aspects: How saving of files executes:
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Overwriting files with entire current ArrayLists every time changes are made.
| Pros | Easier to implement when it comes to delete commands as there is no need to loop through the whole ArrayList to find and compare the object to delete and update files. |
| Cons | Takes more time to load and save. |
- Alternative 2: Appending the new changes to the files every time changes are made.
| Pros | Faster as there is no need to go through the whole ArrayList whenever we save since changes are appended individually. |
| Cons | Difficult and slower to implement for commands that require deletion of objects. |
4.4.2. Save current state
The save current state feature allows the user to store the current state of the program data into the backup storage files. The contents of the backup storage files will be updated and replaced with the current state when save command is implemented by the user.
Implementation
The following steps explain how save command works:
- The user enters
save KitchenHelpercallsParser#parseUserCommand()which splits the user’s input into 2 parts and enters a switch case for execution.parseUserCommandin the Parser object will call a methodSaveStateCommand.- On execute(),
Storage.copyFile()will be called four times to copy contents of ingredients, recipes, chores and expenditure save files into their respective backup storage files.
Design considerations:
Aspects: How saving of current state data executes:
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Using Files.copy to copy content of auto-save files to manual-save files.
| Pros | Easy to implement as less code is needed with Java 7 Files helper class. |
| Cons | Relatively slow copy performance when file size increases. |
- Alternative 2: Using FileChannels to copy content of auto-save files to manual-save files.
| Pros | The FileChannels technique is usually faster than its alternatives such as basic streams. |
| Cons | It may fail for very large files and more lines of codes are needed for implementation. |
4.5. Expenditure
4.5.1. Display Expenditure
The feature for displayexpenditure allows the user to keep track of their total expenditure and the amount they used in their cooking each week.
Implementation
When the user attempts to display expenditure, the Kitchen Helper, Parser and DisplayExpenditureCommand class will be called upon. The following sequence of steps will then occur:
- The user keyed in
displayexpenditure.- A
UIobject will be created and callsUI#getUserCommand(). - Input will be parsed in
Parser#parseUserCommand()and identified with the keyworddisplayexpenditure.
- A
- Parsing of user input and creation of command object
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string in
Parser#prepareDisplayExpenditure()to ensure the parameters are empty, or an exception will be thrown. - The
DisplayExpenditureCommandobject will be created.
- This will automatically trigger the parsing of the user’s input string in
- Executing Command
- The newly created object will call
DisplayExpenditureCommand#execute()which will format the expenditure information into how it will be displayed. - Lastly, a String called
feedbackToUsercontaining the information to display will be returned toKitchenHelper.
- The newly created object will call
- The expenditure information will then be printed onto the console using
Ui#showResultToUser(result).
Design considerations:
- Alternative 1(current implementation): Create a class to handle display of expenditure.
| Pros | More OOP. displayexpenditure is a supported user command so it should have its own class for its specific function just like other commands. |
| Cons | Very abstract method and a lot of effort in order to print the value of two variables. |
- Alternative 2: Have a method to display expenditure in
Parserclass.
| Pros | Simpler and more basic implementation. |
| Cons | Less OOP and will ruin the code style because its execution would be different from other commands. |
4.5.2. Expenditure functionality
The Expenditure function mainly keeps track of two variables, totalExpenditure and amountUsedInCooking. Total expenditure is the amount spent on purchase of ingredients for the week. Amount used in cooking indicates the price of all the ingredients used for cooking or consumption in the week. The latter variable reflects the extent to which the user makes use of his purchase and hence the amount of expenditure he benefited from.
Implementation
The values of the variables in Expenditure change in the the following situations:
- The user executes
addingredient.- During the execution of
Parser#prepareAddIngredient,Expenditure#addToExpenditureretrieves the price and quantity values of the ingredient being added. totalExpenditurevalue increases by the value calculated byExpenditure#addToExpenditure.Storage#saveExpenditureDatasaves the updated value.
- During the execution of
- The user executes
cookrecipe.- During the execution of
CookRecipeCommand#checkIfIngredientExpired,Expenditure#addAmountForCookingretrieves the quantity used in cooking for each ingredient in the recipe. amountUsedInCookingvalue increases by the value calculated byExpenditure#addAmountForCooking.Storage#saveExpenditureDatasaves the updated value.
- During the execution of
- The user executes
deleteingredient.- During the execution of
DeleteIngredientCommand#updateNewQuantityandDeleteIngredientCommand#deleteIngredient,Expenditure#editExpenditureretrieves the quantity of the ingredient to delete. Expenditure#editExpenditurefirst executesExpenditure#removeFromExpenditure, which prompts the user whether the user would like to deduct the cost of the ingredient being deleted from the total expenditure, in the case the user is deleting the ingredient due to wrong addition and would not like to count its cost in total expenditure.- If the user responds with
yes, thetotalExpenditurevalue is decreased by the amount calculated byExpenditure#changePrice. - If the user responds with
no,Expenditure#editExpenditurewill then executeExpenditure#addToAmountUsed, which prompts the user whether the user would like to add the cost of the ingredient being deleted to the amount used in cooking, in the case the user manually deletes ingredients that have been cooked or consumed. - If the user responds with
yes, theamountUsedInCookingvalue increases by the amount calculated byExpenditure#changePrice. - If the user responds with
no, thetotalExpenditurevalue andamountUseInCookingvalue remain unchanged. Storage#saveExpenditureDatasaves the updated value.
- During the execution of
Design considerations:
Aspect: Singleton pattern for Expenditure class.
- Alternative 1(current implementation): Making Expenditure a Singleton.
| Pros | The Expenditure values are accumulated, so the exact same variables have to be used every time. Using only one instance of the Expenditure object allows that. |
| Cons | 1. Increases dependencies as it has a global state. It can be overused and be hard to track. 2. Makes testing harder. |
- Alternative 2: Making Expenditure variables and methods static.
| Pros | Static variables can also update expenditure using the exact same variables. |
| Cons | Take up memory as they cannot be created and destroyed during program execution. |
- Alternative 3: Loading expenditure values from expenditure output text file to a local variable every time.
| Pros | Also allows the retrieval of most updated value. |
| Cons | A lot of storing and loading to and from text files, which increases overhead. |
Aspect: Storage of Expenditure data in its own output file.
- Alternative 1(current implementation): Storage in its own Expenditure output file.
| Pros | Neater to have a specific output file solely for Expenditure data. |
| Cons | Create an entire storage function and output file for three variables. |
- Alternative 2: Storage together with Chore data.
| Pros | Does not require additional storage implementation and save space not creating another file. |
| Cons | Whenever save Expenditure data, the whole data file overwritten and need to loop through entire choreList to save Chore data with the new Expenditure data. |
4.6. Logging
Logging in the application refers to storing exceptions, warnings and messages that occur during the execution of Kitchen Helper. It was included to help developers to identify bugs and to simplify their debugging process.
The java.util.logging package in Java is used for logging. The logging mechanism can be managed from the KitchenHelper class through the kitchenLogs logger object.
All control of the logger for the application can be viewed/ altered in the setUpLogger() method. The current settings for the logger are as follow:
- All logs of
Level.SEVERElevel will be shown on the console when an input/ program flow has caused a possible disruption to the execution of the program. (See the levels of logging below) - All information above ‘Level.FINE’ level is logged into a log file,
KitchenLogs.log. - Logging is made to be displayed in the
SimpleFormatterstyle where the date, class and error description are logged.
Logging Levels:
Level.SEVERE: a serious failure, which prevents normal execution of the program, for end users and system administrators.Level.WARNING: a potential problem, for end users and system administrators.Level.INFO: reasonably significant informational message for end users and system administrators.Level.CONFIG: hardware configuration, such as CPU type.Level.FINE,Level.FINER,Level.FINEST: three levels used for providing tracing information for the software developers.
Additional logging can be done by adding the calling of the global logger and invoking the function log(). This will ensure that all loggings will be made to the same file across the various classes.
An example is shown below:
public static final Logger kitchenLogs = Logger.getLogger(Logger.GLOBAL_LOGGER_NAME);
kitchenLogs.log(Level.WARNING, description_of_warning_here, e.toString());
Appendices
Appendix A: Product Scope
Target user profile:
- Prefers desktop application over other types.
- Can type fast.
- Prefers typing over mouse input.
- Comfortable with using command line interface.
- Facilitate user to track kitchen related information easily.
- Enables user to remove consumed items easily.
- Reminds user of soon perishable food items.
- Reminds user to stock up enough food.
Value proposition: Manage food inventory quickly compared to a typical mouse or graphic user interface driven application which saves time and makes it more convenient.
Appendix B: User Stories
| Version | As a … | I want to … | So that I can … |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1.0 | housewife | add my groceries to the inventory | track my ingredients. |
| v1.0 | user | track the list of ingredients | stock up before I cook a meal. |
| v1.0 | user | delete an ingredient | so that i can remove the wrongly keyed item. |
| v1.0 | user | decrease the quantity of an item in the inventory | see it reflects the current amount after consuming. |
| v1.0 | user | create new recipes | keep a list of recipes in the application. |
| v1.0 | user | view the list of recipe | view the ingredients that are needed for the recipe. |
| v1.0 | user | delete the recipe | remove unwanted recipe. |
| v1.0 | housewife | add chore to the list | remind myself of the tasks that needs to be completed. |
| v1.0 | housewife | be able to see the chore list | check what is not completed. |
| v1.0 | housewife | remove the task | delete a task that was keyed wrongly.. |
| v1.0 | user | save all my ingredients | keep track of them when the application reloads. |
| v1.0 | user | save all my recipes | choose which recipe that i would like to cook when the application reloads. |
| v1.0 | user | save all my chores | view the chores that need to be done. |
| v1.0 | frequent user | view all my past data | get the latest update on my inventory when the application reloads |
| v1.0 | new user | view more information about the commands | learn to use the various commands. |
| v2.0 | user | search for a specific ingredient | view the details regarding the ingredient. |
| v2.0 | user | search the relevant recipe using a keyword | view the different recipe that are similar. |
| v2.0 | user | search for a chore using a keyword | view the status of the chore. |
| v2.0 | user | create unique recipe names | differentiate between my recipes. |
| v2.0 | user | choose a recipe that contains sufficient ingredients | keep track of my ingredients and cook this meal. |
| v2.0 | user | deduct the ingredients that i have from the recipe that i want to cook | save time from deleting manually. |
| v2.0 | housewife | mark the task as done | track the uncompleted task. |
| v2.0 | user | retrieve all of my past history that i have entered in the application | view them again. |
| v2.0 | user | reset all my ingredients, chores, recipes | restart the application. |
| v2.0 | user | deduct ingredients that expire first | do not waste my ingredients. |
| v2.0 | user | be informed if I have sufficient ingredients to cook a specific recipe | find other recipes to cook. |
| v2.0 | user | get the expenditure on the ingredients that I used to cook in the recipe | keep track of my expenditure. |
| v2.0 | user | get the expenditure on the ingredients that I used to cook | keep track of my expenditure. |
Appendix C: Value proposition - Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is Kitchen Helper and the Actor is the user, unless otherwise stated)
Use case: UC01 - Add an ingredient
MSS:
1. User purchases an ingredient.
2. User wants to add to System for tracking purposes.
3. System adds the ingredient.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
2a. System detects invalid format in the entered data.
2a1. System throws invalid input format and shows a valid format example.
Use case resumes at step 2.
2b. System detects zero quantity in the entered data.
2b1. Systems alerts you to enter a quantity more than zero.
Use case resumes at step 2.
2c. System detects a expired expiry date in the entered data.
2c1. System alerts you that Expired ingredient detected in input. Please enter a non-expired expiry
date.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: UC02 - Search for ingredient
MSS:
1. User wants to find ingredients.
2. User enters a keyword in the System.
3. System displays the ingredient related to the keyword.
Extentions:
3a. No matching ingredients related to the keyword.
3a1. Systems show no matching ingredient message
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC03 - Search for recipe
MSS:
1. User wants to find similar recipes.
2. User enters a keyword in the System.
3. System displays the recipe's name related to the keyword.
Use case ends.
Extentions:
3a. No matching recipe related to the keyword.
3a1. Systems show no matching recipe message
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC04 - Search for chore
MSS:
1. User wants to find chores.
2. User enters a keyword in the System.
3. System displays the chore related to the keyword.
Use case ends.
Extentions:
3a. No matching chore related to the keyword.
3a1. Systems show no matching chore message
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC05 - Delete an ingredient
MSS:
1. User wants to delete a particular ingredient.
2. User can either enter a keyword to search in Kitchen Helper or list all ingredients to find the
ingredient to delete.
3. User makes use of the index received in step 2 to delete the ingredient.
4. Kitchen Helper will display a successful message if deletion was successful.
Use case ends.
Extentions:
4a. No matching ingredient related to the index.
4a1. Kitchen Helper will show an error message stating that there is no such ingredient.
Use case resumes at step 3.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC06 - Delete a recipe
MSS:
1. User wants to delete a particular recipe.
2. User can either enter a keyword to search in Kitchen Helper or list all recipes
to find the recipe to delete.
3. User makes use of the index or name received in step 2 to delete the recipe.
4. Kitchen Helper will display a successful message if deletion was successful.
Use case ends.
Extentions:
4a. No matching ingredient related to the index or name.
4a1. Kitchen Helper will show an error message stating that there is no such recipe.
Use case resumes at step 3.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC07 - Cook a recipe
MSS:
1. User wants to cook a recipe for a number of pax.
2. User can search for the recipe that it wants to cook.
3. User use the name obtained in step 2 to cook the recipe.
4. Kitchen Helper will display a successful message if it was able to cook the recipe.
Use case ends.
Extentions:
4a. There are insufficient/missing ingredients in the ingredients' inventory.
4a1. Kitchen Helper will show an error message stating that there were insufficient/missing
ingredients to cook the recipe.
4b. There are insufficient ingredients due to some expired ingredients in the ingredients' invenory.
4b1. Kitchen Helper will show an error message and a list of expired ingredients.
Use case resumes at step 3.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC08 - List Ingredients
MSS:
1. User wants to see the whole ingredient list.
2. User use the category 'all' to display whole ingredient list.
3. System displays all ingredients regardless of category.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
2a. System detects invalid format in the entered data.
2a1. System throws invalid input format and shows a valid format example.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: UC09 - List Ingredients from Meat category
MSS:
1. User wants to see the whole ingredient list.
2. User use the category 'meat' to display whole ingredient list.
3. System displays ingredients under the category, `meat`.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
2a. System detects invalid format in the entered data.
2a1. System throws invalid input format and shows a valid format example.
2b. System detects invalid category in the entered data.
2b1. System throws invalid category name and shows the valid category names.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: UC10 - List Recipe name
MSS:
1. User wants to see the whole list of Recipe name.
2. User use the category 'all' to display whole recipe name list.
3. System displays all recipe name.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
2a. System detects invalid format in the entered data.
2a1. System throws invalid input format and shows a valid format example.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: UC11 - List of Ingredients in Recipe
MSS:
1. User wants to see the ingredient list inside a Recipe.
2. User use the recipe number '1' to display the ingredient list needed to cook the recipe.
3. System displays all ingredients under the recipe.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
2a. System detects invalid format in the entered data.
2a1. System throws invalid input format and shows a valid format example.
Appendix D: Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - An user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Should not require user to install program file.
- Should work for single user.
- Should be able to run without internet connection.
Appendix E: Glossary
- Category - The group of the ingredient belongs to
- Price - Unit cost of a single quantity
- Expiry - The expiry date of the ingredient
- Mainstream OS - Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
Appendix F: Instructions for Manual Testing
F.1. Launch and Shutdown
- Initial launch
- Download the jar file, renamed it to
kitchenhelperand copy into an empty folder. - Open up command prompt or terminal.
- Change directory to where the jar file is located.
- Run the command
java -jar kitchenhelper.jar
Expected: Shows a message to load data from normal mode or restore mode.
- Download the jar file, renamed it to
F.2. Add an ingredient
- Add an ingredient into Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: List all the ingredient using the
listingredient allcommand. - Test case:
addingredient /n beef /c meat /q 3 /p 20 /e 03/03/2022
Expected: Entry can be seen usinglistingredient allcommand. - Test case:
addingredient /n chicken /c meat /q 3 /p 3 /e 03/03/2020
Expected: Expired ingredient detected in input.
Please enter a non-expired expiry date. - Test case:
addingredient /n milo /c drink /q 0 /p 1 /e 03/03/2022
Expected: Please enter a quantity more than 0.
- Prerequisites: List all the ingredient using the
F.3. List ingredient
- List Ingredient
- Prerequisites: Add ingredient using the
addingredient /n beef /c meat /q 3 /p 20.20 /e 03/03/2022command. - Test case:
listingredient all
Expected: Entry can be seen usinglistingredient allcommand and all other categories. - Test case:
listingredient meat
Expected: Entry can be seen usinglistingredient allcommand and onlymeatcategory is shown. - Test case:
listingredient 1
Expected: Invalid Command, please check your format! - Test case:
listingredient airplane
Expected: Invalid Command, please check your format!
- Prerequisites: Add ingredient using the
F.4. Delete an ingredient
- Delete an ingredient from Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: List all the recipes using the
listingredient allcommand. - Test case (if ingredient index exists):
deleteingredient /i 1
Expected: The ingredient will be deleted. It can be noticed by using thelistingredient allcommand. - Test case (if ingredient index does not exists):
deleteingredient /i -1
Expected: No ingredients are deleted. It can be noticed by using thelistingredient allcommand. - Test case (if there is sufficient quantity to be reduced from the ingredient):
deleteingredient /i 1 /q 2
Expected: The quantity of the ingredient will change as seen by usinglistingredient allcommand. - Test case (if there are insufficient quantity to be reduced from the ingredient):
deleteingredient /i 1 /q 10
Expected: The quantity of the ingredient will not changed as seen by usinglistingredient allcommand. - Test case (if the quantity of the ingredient is reduced to zero after deduction):
deleteingredient /i 1 /q 1
Expected: The ingredient will be deleted as its final quantity is zero. This can be noticed by usinglistingredient allcommand.
- Prerequisites: List all the recipes using the
F.5. Search for ingredient
- Search for ingredients in Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: The ingredient list should not be empty. You should at least add the following ingredient by using
addingredient /n beef /c meat /q 3 /p 20 /e 03/03/2022before the search. - Test case:
searchingredient beef
Expected: Ingredient entries that have the keyword matchingbeefnames are listed. - Test case:
searchingredient meat
Expected: Ingredient entries that have the keyword matchingmeatcategory are listed. - Test case:
searchingredient 03/03/2022
Expected: Ingredient entries that have the keyword matching03/03/2022date are listed. - Test case:
searchingredient $20
Expected: Ingredient entries that have the keyword matching$20price are listed.
- Prerequisites: The ingredient list should not be empty. You should at least add the following ingredient by using
F.6. Add a recipe
- Add a recipe into Kitchen Helper
- Prerequisites: List all the recipes using the
listrecipe allcommand. - Test case:
addrecipe /n warm milk /i HL Milk:1:Dairy
Expected: Entry can be found usinglistrecipe allcommand.
- Prerequisites: List all the recipes using the
F.7. List recipe
- List Recipe
- Prerequisites: Add ingredient using the
addrecipe /n warm milk /i HL Milk:1:Dairycommand. - Test case:
listrecipe all
Expected: Entry can be seen usinglistrecipe allcommand, shows all recipe’s name added. - Test case:
listrecipe 1
Expected: Entry can be seen usinglistrecipe 1command and shows all ingredients registered in the recipe. - Test case:
listrecipe 2
Expected: The Recipe List is currently empty. - Test case:
listrecipe notsure
Expected: Invalid Command, please check your format!
- Prerequisites: Add ingredient using the
F.8. Cook a recipe
- Cooks the specified recipe and ingredients in the recipe will be automatically deducted.
- Prerequisites: List all the recipes using the
listrecipe allcommand. - Test case (sufficient ingredient):
cookrecipe /n warm milk /p 2
Expected: A reduction of the ingredients’ quantity multiplied by2can be noticed when listing the ingredients withlistingredient all - Test case (Sufficient even with expired ingredients):
cookrecipe /n warm milk /p 2
Expected: The automatic deduction will not be carried out and expired item will be notified to user. - Test case: (Insufficient even with expired ingredients):
cookrecipe /n warm milk /p 2
Expected: The automatic deduction will not be carried out.
- Prerequisites: List all the recipes using the
F.9. Delete a recipe
- Delete a recipe from Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: List all the recipes using the
listrecipe allcommand. - Test case (if recipe index or name exists):
deleterecipe /i 1ORdeleterecipe /i warm milk
Expected: The recipe will be deleted. It can be noticed by using thelistrecipe allcommand. - Test case (if recipe index or name does not exists):
deleterecipe /i -1ORdeleterecipe /n Beef Stew
Expected: No recipes are deleted. It can be noticed by using thelistrecipe allcommand.
- Prerequisites: List all the recipes using the
F.10. Search for recipe
- Search for similar recipe in Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: The recipe list should not be empty. You should at least add the following recipe by using
addrecipe /n Chicken Salad /i Chicken Breast:2:meat, Lettuce:4:vegetablebefore the search. - Test case:
searchrecipe chicken
Expected: Recipe’s name entries that have the keyword matching `chicken’ are listed.
- Prerequisites: The recipe list should not be empty. You should at least add the following recipe by using
F.11. Add a chore
- Adds a chore into Kitchen Helper.
- Test case (String deadline):
addchore buy groceries /by Monday 12pm
Expected: The chore is added. Entry can be found usinglistchorecommand. - Test case (Date deadline):
addchore buy groceries /by 13/04/2020 12:00
Expected: The chore is added. Entry can be found usinglistchorecommand. - Test case (Incorrect date format):
addchore buy groceries /by 13-04-2020
Expected: Deadline will be a String object type. The chore is added. Entry can be found usinglistchorecommand. - Test case (Invalid format):
addchore buy groceries
Expected: The chore is not added. Entry cannot be found usinglistchorecommand.
- Test case (String deadline):
F.12. List a chore
- List the chores.
- Test case (Empty list):
listchore
Expected: “Your list of chores is currently empty.” - Test case (Non-empty list):
listchore
Expected: All the chore entries displayed. - Test case (Invalid format):
listchore aa
Expected: “Invalid ListChore command.” No chore entries displayed.
- Test case (Empty list):
F.13. Delete a chore
- Delete a chore from Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: List all the chores using
listchorecommand. - Test case (Index in list):
deletechore 1
The chore is deleted. It can be noticed by using thelistchorecommand. - Test case (Index not in list or incorrect format):
deletechore 10ORdeletechore -1ORdeletechore buy groceries
Expected: The chore is not deleted. It can be noticed by using thelistchorecommand.
- Prerequisites: List all the chores using
F.14. Search for chore
- Search for chores in Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: The chore list should not be empty. You should at least add the following chore by using
addchore buy groceries /by Tuesday 12pmbefore the search. - Test case:
searchchore groceries
Expected: Chore entries that have the keyword matchinggroceriesdescription are listed. - Test case:
searchchore Tuesday
Expected: Chore entries that have the keyword matchingTuesdayas a string are listed.
- Prerequisites: The chore list should not be empty. You should at least add the following chore by using
F.15. Mark a chore as done
- Change the completion status of a chore to done.
- Prerequisites: List all the chores using
listchorecommand. - Test case (Index in list):
done 1
Expected: The chore is marked as done. The completion status icon becomes a tick. - Test case (Mark an already complete chore):
done 1
Expected: “This chore has already been marked as done.” - Test case (Index not in list or incorrect format):
done 10ORdone -1ORdone buy groceries
Expected: The chore is not marked as done. It can be noticed by using thelistchorecommand where the completion status icon of the chore remains a cross.
- Prerequisites: List all the chores using
F.16. Saving data
- Load ingredient data into Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: The ingredient list save file should not be empty.
- Expected: Previously stored ingredient data can be seen using
listingredient allcommand.
- Load recipe data into Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: The recipe list save file should not be empty.
- Expected: Previously stored recipe data can be seen using
listrecipe allcommand.
- Load chore data into Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: The chore list save file should not be empty.
- Expected: Previously stored chore data can be seen using
listchorecommand.
- Load expenditure data into Kitchen Helper.
- Prerequisites: The expenditure save file should not be empty.
- Expected: Previously stored expenditure data of the week can be seen using
displayexpenditurecommand.
If any of the save files are empty, the user can choose to populate the files with their own user commands or alternatively, use any of the test cases below:
addrecipe /n Chicken Salad /i Chicken Breast:2:meat, Lettuce:4:vegetableaddingredient /n Chicken Breast /c meat /q 3 /p 20 /e 18/12/2020addingredient /n kailan /c Vegetable /q 30 /p 30.45 /e 12/12/2020addingredient /n HL Milk /c Dairy /q 3 /p 12.2 /e 14/12/2020addchore buy groceries /by Tuesday 12pm
Note that expenditure changes when addingredient, deleteingredient, or cookrecipe commands are used.
F.17. Display expenditure
- Displays user expenditure.
- Prerequisite 1: Add an ingredient using
addingredientcommand. - Test case 1:
displayexpenditure
Expected: The value of total expenditure increases by the cost of ingredient multiplied by its quantity. - Prerequisite 2: Cook a recipe using
cookrecipecommand. - Test case 2:
displayexpenditure
Expected: The value of amount used in cooking increases by the cost of all the ingredients used in cooking. - Prerequisite 3: Delete an ingredient using
deleteingredientcommand and respond withyeswhen prompted to remove cost of ingredient from total expenditure . - Test case 3:
displayexpenditure
Expected: The value of total expenditure decreases by the cost of ingredient multiplied by the quantity deleted. - Prerequisite 4: Delete an ingredient using
deleteingredientcommand and respond withnowhen prompted to remove cost of ingredient from total expenditure and respond withyeswhen prompted to add cost of ingredient to amount used in cooking. - Test case 4:
displayexpenditure
Expected: The value of amount used in cooking increases by the cost of ingredient multiplied by the quantity deleted.
- Prerequisite 1: Add an ingredient using